This file contains curated lists of machine learning terms which the ML enthusiasts find difficult in understanding. The terms are
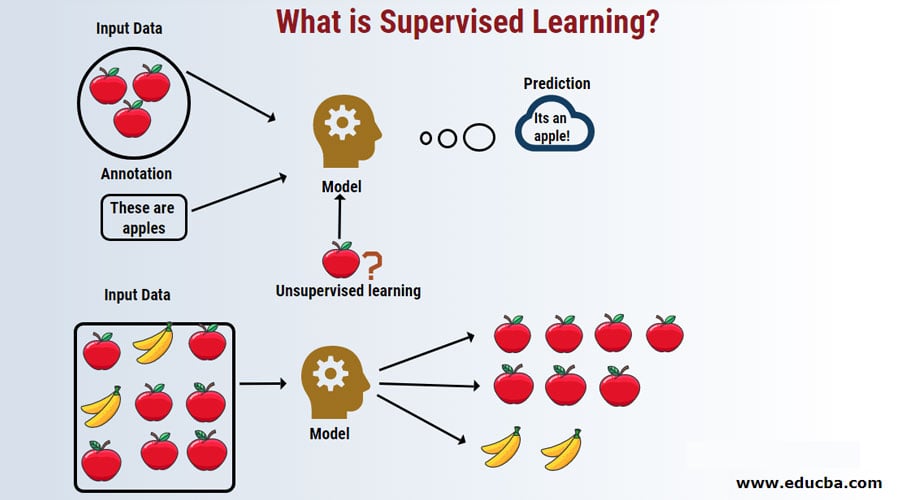
- You get a bunch of photos with information about what is on them and then you train a model to recognize new photos.
- You have a bunch of molecules and information about which are drugs and you train a model to answer whether a new molecule is also a drug.

A.) let's take a real-life scenario- When you try to warn a kid to not touch fire because it will hurt, you are "supervising" the learning of the kid. This is supervised machine learning.
B.)When the kid tries to touch the fire anyway and jumps back due to the burning sensation. The kid(agent) is interacting with the fire(environment) and learns that it is not good to touch fire. This is unsuperised learning as the kid himself is learning the action.
C.)Hence, the kid is not going to touch the fire again due to the pain(penalty) experienced and decides the next action "stay away from fire" in order to be safe and happy(reward). This is Reinforcement Machine Learning.
EXAMPLES: Self driving cars, in NLP (Natural Language Processing), news recommendation, Amazon /flipcart product recommendations,
Machine is trained to predict some quantitites like price, weight or height.
predicting house/property price, forecasting stocks, forecasting weather, predicting stock market price etc.
Clustering can be understood with the help of clusters. So a CLUSTER is a group of objects which are similar in some ways. It is used to find a pattern in Machine Learning. It is a part of unsupervised learning so deals with the unlabelled dataset. In layman it is method of grouping objects (similar in some way) called clusters. It does it by finding some similar patterns in the unlabelled dataset such as shape, size, color, behavior, etc., and divides them as per the presence and absence of those similar patterns.
EXAMPLE: Netflix recommendation systems- With the help of clustering, Netflix data scientists find people who like the series "Lost", "Black Mirror" and "Groundhog Day". Then it is used to refine its knowledge of the tastes of viewers and thus make better decisions in the creation of new original series.
News Recommedation system- Like news is shown in different categroies. Like your searched sports news on google, so clustering method will make cluster /group of sports news. Then it is shown in the search results
Machine is trained to classify something into some class. So in layman classification includes those problems which has a certain answer like YES OR NO. EXAMPLE: classifying whether a patient has disease or not, classifying whether an email is spam or not, classifying whether your pass or fail in your exams. It is a part of supervised learning.
CLUSTERING vs CLASSIFICATION SOURCE: https://blog.bismart.com/en/classification-vs.-clustering-a-practical-explanation
Linear Regression algorithm will use the data points to find the best fit line to model the data. A line can be represented by the equation, y = m*x + c where y is the dependent variable and x is the independent variable. Basic calculus theories are applied to find the values for m and c using the given data set. Linear Regression has 2 types as Simple Linear Regression where only 1 independent variable is used and Multiple Linear Regression where multiple independent variables are defined.
Learn more here
Polynomial regression is generally studied after clearing the concepts of Linear Regression. Now, as we know that liner regression is effective when there is a linear relationship between the features but most of the times this condition does not hold true so instead a Polynomial regression model is used. Here the main advantage of using the polynomial regression algorithm is that it provides the best aproximate relationship in between the dependent and the independent varibale and the main disadvantage is that one or two outliers in the data can seriously affect the results of the nonlinear analysis.
It is a type of model that is basically used to produce binary output. In this model a logistic function is used to model a binary dependent variable but this is just the most basic type and many more complex models do exist. Surprisingly enough despite having "regression" in it's name Logistic regression can not be used for regression type problems can be used only for performing classification tasks or in technincal terms it is used to predict categorical variables and not the continuous dependent variables. Although it is a binary classifier it is also used for multi class calssification as, let us consider an example where we have 4 categorical variables then we will first see if the first data point is classified as 1st or not if it is not then it is checked for the second categorical variable and so on till we get the correct class that the data point belongs to it is somewhat similar to the if-else condition. ** For getting a deeper insight reffer to the link provided: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_regression **
This algorithm is mainly studied after clearing the concepts of Linear and Logistic Regression, it is highly preferred by many as it produces significant accuracy with less computation power. It can be used for both classification and regression task but it is widely used in classification tasks. The objective of SVM algorithm is to find a hyperplane in an N-dimensional space(N — the number of features) that distinctly classifies the data points. In 2 dimensional space the seperating medium is a line and in 3 dimensional space the seperating medium is a plane and for more than 3 dimensions we call it a hyperplane. It works bets on small datasets with high dimensionality. ** For deeper insight please reffer to the link provided: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/09/understaing-support-vector-machine-example-code/