Sara Venkatraman 1/12/2021
First we run a script which reads the syndromic surveillance data, and we also load a few libraries.
# Load script which reads the syndromic surveillance data and sets up the design matrices used for modeling
source("ModelingSetup.R")
# Packages for obtaining robust standard errors and VIFs
library(lmtest); library(sandwich); library(car); library(MASS)
# Packages for spatiotemporal modeling
library(maptools); library(spdep); library(INLA)
# Packages for plotting and printing tables
library(ggplot2); library(gridExtra); library(knitr)Now we read in a zip code-level NYC shapefile that will later enable us to construct spatiotemporal models of case counts over time and over 173 zip codes.
## Reading layer `tl_2010_36_zcta510NYC' from data source `/Users/saravenkatraman/Documents/Cornell University (PhD)/Research/COVID-19 Demographics/Paper 1 Surveillance Analysis/Spatiotemporal Model Files/tl_2010_36_zcta510NYC.shp' using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
## Simple feature collection with 226 features and 12 fields
## geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
## dimension: XY
## bbox: xmin: 913090.7 ymin: 120053.5 xmax: 1080968 ymax: 283594.7
## projected CRS: NAD83 / New York Long Island (ftUS)
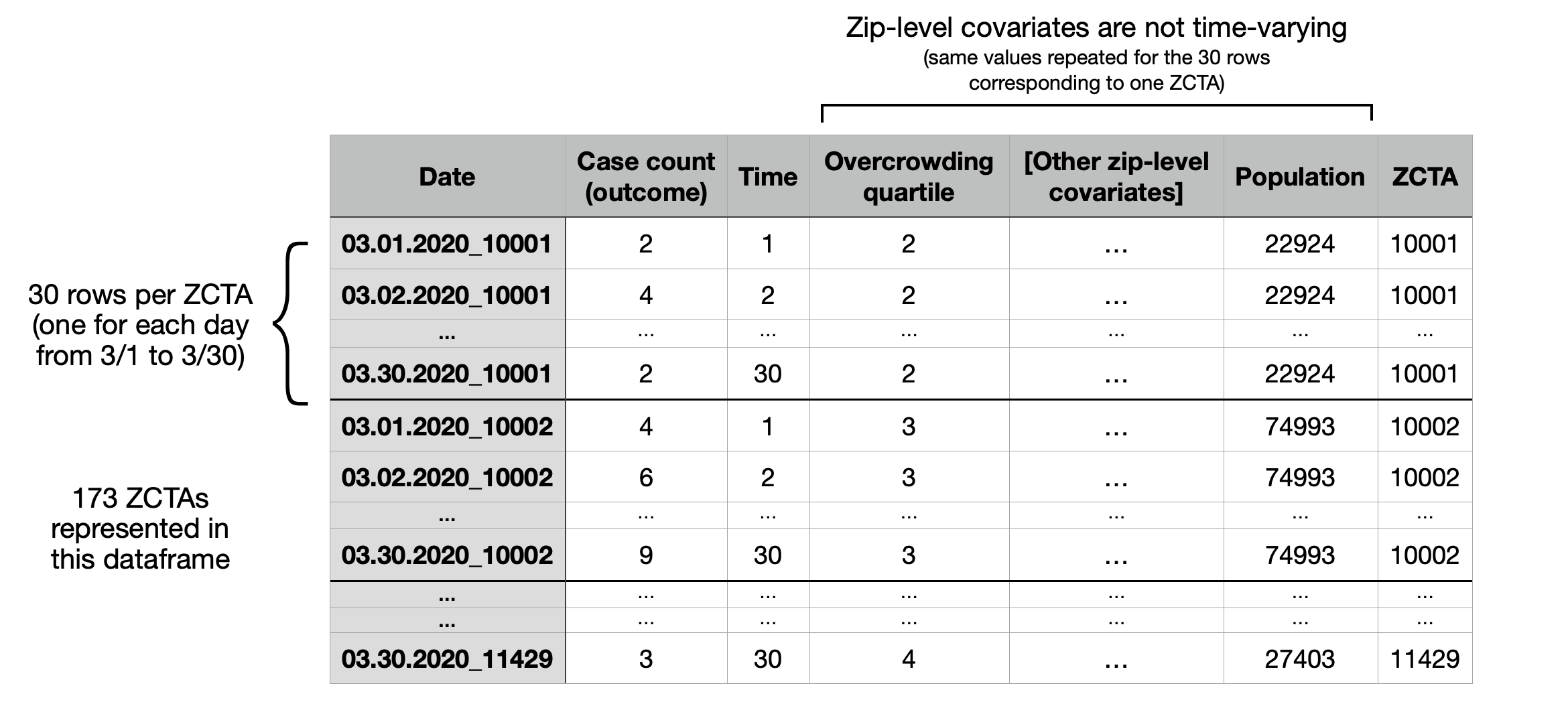
The next few lines of code produce a dataframe (“design matrix”) of the following form. Below, “Case count” refers to the suspected cases, i.e. the total number of ILI + pneumonia emergency department presentations observed on that day. In this dataframe, both overcrowdedness and multigenerational housing are binned into quartiles.
# Design matrix construction
designResponse.ili <- Concatenate.Zipcode.Data(zctaOrder, "influenza", "2020-03-16", variablesToDiscretize=c("PctOvercrowded", "PctMultigen"), quartile=T)
designResponse.pneu <- Concatenate.Zipcode.Data(zctaOrder, "pneumonia", "2020-03-16", variablesToDiscretize=c("PctOvercrowded", "PctMultigen"), quartile=T)
designResponse <- cbind(designResponse.ili$Count + designResponse.pneu$Count, designResponse.ili[,-1])
colnames(designResponse)[1] <- "Count"; remove(designResponse.ili); remove(designResponse.pneu)
# Get sum of essential employment percentages
designResponse$PctEssEmpl <- rowSums(designResponse[,18:23])Define functions for neatly printing the model coefficients and confidence intervals. The first function applies to GLMs and the second applies to INLA models.
Print.Model.Results.GLM <- function(modelGLM, numDecimal) {
# Get coefficient estimates and confidence intervals. Combine them (along with the)
# p-value) into one table, called 'modelResults' - results rounded to 'numDecimal'
modelCoef <- coeftest(modelGLM)
modelCI <- coefci(modelGLM, vcov=vcovHC(modelGLM, type="HC3"))
modelResults <- cbind(round(exp(modelCoef[,1]), numDecimal),
modelCoef[,4],
round(exp(modelCI[,1:2]), numDecimal))
colnames(modelResults)[1:2] <- c("exp(Estimate)", "p-value")
# Create a 1-column table called 'resultsSummary' that stores model results in
# the following format: "exp(Estimate), (ciLower, ciUpper)"
resultsSummary <- matrix("", nrow=nrow(modelResults), ncol=1)
rownames(resultsSummary) <- rownames(modelResults)
for(i in 1:nrow(modelResults)) {
string.i <- paste(modelResults[i,1], " (", modelResults[i,3], ", ", modelResults[i,4], ")", sep="")
resultsSummary[i,1] <- string.i
}
resultsSummary <- resultsSummary[c(3:nrow(resultsSummary), 2, 1), ]
return(modelResults)
}
Print.Model.Results.INLA <- function(modelINLA, numDecimal) {
# Get coefficient estimates and confidence intervals. Combine them (along with the)
# p-value) into one table, called 'modelResults' - results rounded to 'numDecimal'
modelResults <- cbind(round(exp(model5.INLA$summary.fixed[,1]), numDecimal),
model5.INLA$summary.fixed[,2],
round(exp(model5.INLA$summary.fixed[,-c(1:2,4,7)]), numDecimal))
colnames(modelResults)[1:2] <- c("exp(Estimate)", "SD")
# Create a 1-column table called 'resultsSummary' that stores model results in
# the following format: "exp(Estimate), (ciLower, ciUpper)"
resultsSummary <- matrix("", nrow=nrow(modelResults), ncol=1)
rownames(resultsSummary) <- rownames(modelResults)
for(i in 1:nrow(modelResults)) {
string.i <- paste(modelResults[i,1], " (", modelResults[i,3], ", ", modelResults[i,4], ")", sep="")
resultsSummary[i,1] <- string.i
}
resultsSummary <- resultsSummary[c(3:nrow(resultsSummary), 2, 1), ]
return(modelResults)
}model1.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. None need to be removed (based on VIF > 10 criterion)
kable(vif(model1.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 1.432021 | 3 | 1.061675 |
| PctMultigen | 1.432021 | 3 | 1.061675 |
# Print model results
kable(Print.Model.Results.GLM(model1.ILIpneu, 2))| exp(Estimate) | p-value | 2.5 % | 97.5 % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.37 | 0e+00 | 0.35 | 0.39 |
| Time | 1.04 | 0e+00 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ2 | 1.56 | 0e+00 | 1.47 | 1.65 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ3 | 1.75 | 0e+00 | 1.66 | 1.85 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ4 | 2.05 | 0e+00 | 1.92 | 2.18 |
| PctMultigenQ2 | 1.19 | 1e-07 | 1.12 | 1.26 |
| PctMultigenQ3 | 1.30 | 0e+00 | 1.22 | 1.37 |
| PctMultigenQ4 | 1.59 | 0e+00 | 1.49 | 1.69 |
model2.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + BPHIGH_CrudePrev + DIABETES_CrudePrev + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + COPD_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. COPD has the largest VIF.
kable(vif(model2.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 2.584312 | 3 | 1.171451 |
| PctMultigen | 3.535624 | 3 | 1.234272 |
| BPHIGH_CrudePrev | 19.596931 | 1 | 4.426842 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 25.024530 | 1 | 5.002452 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 21.534671 | 1 | 4.640546 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 8.007129 | 1 | 2.829687 |
| COPD_CrudePrev | 42.218345 | 1 | 6.497565 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 25.581867 | 1 | 5.057852 |
# Re-fit model without COPD
model2.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + BPHIGH_CrudePrev + DIABETES_CrudePrev + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. Hypertension now has the largest VIF.
kable(vif(model2.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 2.493952 | 3 | 1.164523 |
| PctMultigen | 3.385975 | 3 | 1.225408 |
| BPHIGH_CrudePrev | 11.208735 | 1 | 3.347945 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 9.748967 | 1 | 3.122333 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 4.412565 | 1 | 2.100611 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 8.007108 | 1 | 2.829683 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 6.169262 | 1 | 2.483800 |
# Re-fit model without COPD and hypertension
model2.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + DIABETES_CrudePrev + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. No more variables need to be removed.
kable(vif(model2.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 1.973983 | 3 | 1.120015 |
| PctMultigen | 3.519230 | 3 | 1.233317 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 6.924940 | 1 | 2.631528 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 3.155821 | 1 | 1.776463 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 3.406973 | 1 | 1.845799 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 4.520681 | 1 | 2.126189 |
# Print model results
kable(Print.Model.Results.GLM(model2.ILIpneu, 2))| exp(Estimate) | p-value | 2.5 % | 97.5 % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.50 | 0.0000000 | 0.44 | 0.57 |
| Time | 1.04 | 0.0000000 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ2 | 1.22 | 0.0000000 | 1.15 | 1.30 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ3 | 1.47 | 0.0000000 | 1.39 | 1.56 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ4 | 1.80 | 0.0000000 | 1.68 | 1.92 |
| PctMultigenQ2 | 1.08 | 0.0399473 | 1.00 | 1.15 |
| PctMultigenQ3 | 1.09 | 0.0281987 | 1.01 | 1.18 |
| PctMultigenQ4 | 1.03 | 0.5593874 | 0.93 | 1.12 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 1.16 | 0.0000000 | 1.14 | 1.18 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 0.72 | 0.0000000 | 0.69 | 0.74 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 1.01 | 0.0000004 | 1.01 | 1.02 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 0.99 | 0.3003368 | 0.98 | 1.01 |
model3.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + PctWhite + PctBelowPovThresh + MedianIncome + PctEssEmpl + PopDensity + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. No variables need to be removed.
kable(vif(model3.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 2.448803 | 3 | 1.160982 |
| PctMultigen | 4.241565 | 3 | 1.272295 |
| PctWhite | 2.933174 | 1 | 1.712651 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 5.209530 | 1 | 2.282439 |
| MedianIncome | 5.831066 | 1 | 2.414760 |
| PctEssEmpl | 2.123767 | 1 | 1.457315 |
| PopDensity | 1.615957 | 1 | 1.271203 |
# Print model results
kable(Print.Model.Results.GLM(model3.ILIpneu, 2))| exp(Estimate) | p-value | 2.5 % | 97.5 % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 2.26 | 0.0000000 | 1.63 | 3.13 |
| Time | 1.04 | 0.0000000 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ2 | 1.37 | 0.0000000 | 1.28 | 1.45 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ3 | 1.43 | 0.0000000 | 1.34 | 1.52 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ4 | 1.62 | 0.0000000 | 1.50 | 1.75 |
| PctMultigenQ2 | 1.02 | 0.6419374 | 0.95 | 1.10 |
| PctMultigenQ3 | 1.09 | 0.0408901 | 1.01 | 1.18 |
| PctMultigenQ4 | 1.29 | 0.0000001 | 1.16 | 1.42 |
| PctWhite | 1.00 | 0.0000000 | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 0.99 | 0.0000000 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| MedianIncome | 1.00 | 0.0000000 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PctEssEmpl | 0.98 | 0.0000000 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| PopDensity | 1.00 | 0.2630634 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
model4.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + BPHIGH_CrudePrev + DIABETES_CrudePrev + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + COPD_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + PctWhite + PctBelowPovThresh + MedianIncome + PctEssEmpl + PopDensity + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. COPD has the largest VIF.
kable(vif(model4.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 3.846854 | 3 | 1.251750 |
| PctMultigen | 6.377466 | 3 | 1.361783 |
| BPHIGH_CrudePrev | 34.934980 | 1 | 5.910582 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 31.422820 | 1 | 5.605606 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 25.819671 | 1 | 5.081306 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 13.682975 | 1 | 3.699051 |
| COPD_CrudePrev | 44.711002 | 1 | 6.686629 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 25.237238 | 1 | 5.023668 |
| PctWhite | 10.953861 | 1 | 3.309662 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 11.427916 | 1 | 3.380520 |
| MedianIncome | 9.110909 | 1 | 3.018428 |
| PctEssEmpl | 2.906632 | 1 | 1.704885 |
| PopDensity | 2.275761 | 1 | 1.508563 |
# Re-fit model without COPD
model4.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + BPHIGH_CrudePrev + DIABETES_CrudePrev + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + PctWhite + PctBelowPovThresh + MedianIncome + PctEssEmpl + PopDensity + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. Hypertension now has the largest VIF.
kable(vif(model4.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 3.741625 | 3 | 1.245977 |
| PctMultigen | 6.076750 | 3 | 1.350865 |
| BPHIGH_CrudePrev | 22.335040 | 1 | 4.725996 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 19.144007 | 1 | 4.375387 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 11.228197 | 1 | 3.350850 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 12.921141 | 1 | 3.594599 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 7.724030 | 1 | 2.779214 |
| PctWhite | 10.708772 | 1 | 3.272426 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 10.301103 | 1 | 3.209533 |
| MedianIncome | 9.039144 | 1 | 3.006517 |
| PctEssEmpl | 2.827104 | 1 | 1.681399 |
| PopDensity | 2.242667 | 1 | 1.497554 |
# Re-fit model without COPD and hypertension
model4.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + DIABETES_CrudePrev + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + PctWhite + PctBelowPovThresh + MedianIncome + PctEssEmpl + PopDensity + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. Diabetes now has the largest VIF.
kable(vif(model4.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 2.946263 | 3 | 1.197325 |
| PctMultigen | 5.636454 | 3 | 1.334036 |
| DIABETES_CrudePrev | 19.141963 | 1 | 4.375153 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 4.798823 | 1 | 2.190622 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 4.608372 | 1 | 2.146712 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 7.704025 | 1 | 2.775613 |
| PctWhite | 7.334862 | 1 | 2.708295 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 9.114278 | 1 | 3.018986 |
| MedianIncome | 8.906441 | 1 | 2.984366 |
| PctEssEmpl | 2.845184 | 1 | 1.686767 |
| PopDensity | 1.952700 | 1 | 1.397390 |
# Re-fit model without COPD, hypertension, and diabetes
model4.ILIpneu <- glm(Count ~ Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + PctWhite + PctBelowPovThresh + MedianIncome + PctEssEmpl + PopDensity + offset(log(Population/10000)), family=quasipoisson, data=designResponse)
# Check variance inflation factors. No more variables need to be removed.
kable(vif(model4.ILIpneu))| GVIF | Df | GVIF^(1/(2*Df)) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.000000 | 1 | 1.000000 |
| PctOvercrowded | 2.940120 | 3 | 1.196908 |
| PctMultigen | 5.494162 | 3 | 1.328363 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 2.361142 | 1 | 1.536601 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 4.401103 | 1 | 2.097881 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 7.489049 | 1 | 2.736613 |
| PctWhite | 3.324916 | 1 | 1.823435 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 8.816106 | 1 | 2.969193 |
| MedianIncome | 8.326959 | 1 | 2.885647 |
| PctEssEmpl | 2.578324 | 1 | 1.605716 |
| PopDensity | 2.003799 | 1 | 1.415556 |
# Print model results
kable(Print.Model.Results.GLM(model4.ILIpneu, 2))| exp(Estimate) | p-value | 2.5 % | 97.5 % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 21.88 | 0.0000000 | 14.50 | 33.01 |
| Time | 1.04 | 0.0000000 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ2 | 1.21 | 0.0000000 | 1.14 | 1.29 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ3 | 1.43 | 0.0000000 | 1.34 | 1.53 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ4 | 1.57 | 0.0000000 | 1.45 | 1.70 |
| PctMultigenQ2 | 1.17 | 0.0000302 | 1.09 | 1.26 |
| PctMultigenQ3 | 1.37 | 0.0000000 | 1.26 | 1.50 |
| PctMultigenQ4 | 1.53 | 0.0000000 | 1.39 | 1.69 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 0.75 | 0.0000000 | 0.73 | 0.78 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 1.03 | 0.0000000 | 1.03 | 1.04 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 0.97 | 0.0001401 | 0.96 | 0.99 |
| PctWhite | 1.00 | 0.7064446 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 0.97 | 0.0000000 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| MedianIncome | 1.00 | 0.0000000 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PctEssEmpl | 0.96 | 0.0000000 | 0.95 | 0.97 |
| PopDensity | 1.00 | 0.4256017 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
# Add zip code ID number to design matrix (needed for spatial and temporal random effects)
zipcodeID <- sort(rep(1:length(allZipcodes), 30))
designResponse$ZipID <- zipcodeID
designResponse$ZipID2 <- zipcodeID
# Construct spatiotemporal model using same set of covariates in (reduced) model 4
model5.INLAformula <- Count ~ 1 + f(ZipID, model="bym", offset(Population/10000), graph=NYCadj) + f(ZipID2, Time, model="rw1") + Time + PctOvercrowded + PctMultigen + CHD_CrudePrev + OBESITY_CrudePrev + CSMOKING_CrudePrev + PctWhite + PctBelowPovThresh + MedianIncome + PctEssEmpl + PopDensity
model5.INLA <- inla(model5.INLAformula, family="poisson", data=designResponse, control.compute=list(dic=TRUE,cpo=TRUE))
# Print model results
kable(Print.Model.Results.INLA(model5.INLA, 2))| exp(Estimate) | SD | 0.025quant | 0.975quant | mode | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 13.04 | 0.7808933 | 2.81 | 60.30 | 13.07 |
| Time | 1.04 | 0.0008200 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.04 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ2 | 1.21 | 0.1268922 | 0.94 | 1.55 | 1.21 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ3 | 1.17 | 0.1367633 | 0.90 | 1.53 | 1.18 |
| PctOvercrowdedQ4 | 1.25 | 0.2022859 | 0.84 | 1.86 | 1.25 |
| PctMultigenQ2 | 1.46 | 0.1624302 | 1.06 | 2.01 | 1.46 |
| PctMultigenQ3 | 1.93 | 0.1870050 | 1.33 | 2.78 | 1.93 |
| PctMultigenQ4 | 1.87 | 0.2217379 | 1.21 | 2.89 | 1.88 |
| CHD_CrudePrev | 0.90 | 0.0557072 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0.90 |
| OBESITY_CrudePrev | 0.99 | 0.0147861 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 0.99 |
| CSMOKING_CrudePrev | 1.09 | 0.0389113 | 1.01 | 1.18 | 1.09 |
| PctWhite | 1.00 | 0.0034791 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PctBelowPovThresh | 0.95 | 0.0126772 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.96 |
| MedianIncome | 1.00 | 0.0000028 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PctEssEmpl | 0.98 | 0.0142962 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.98 |
| PopDensity | 1.00 | 0.0000018 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |