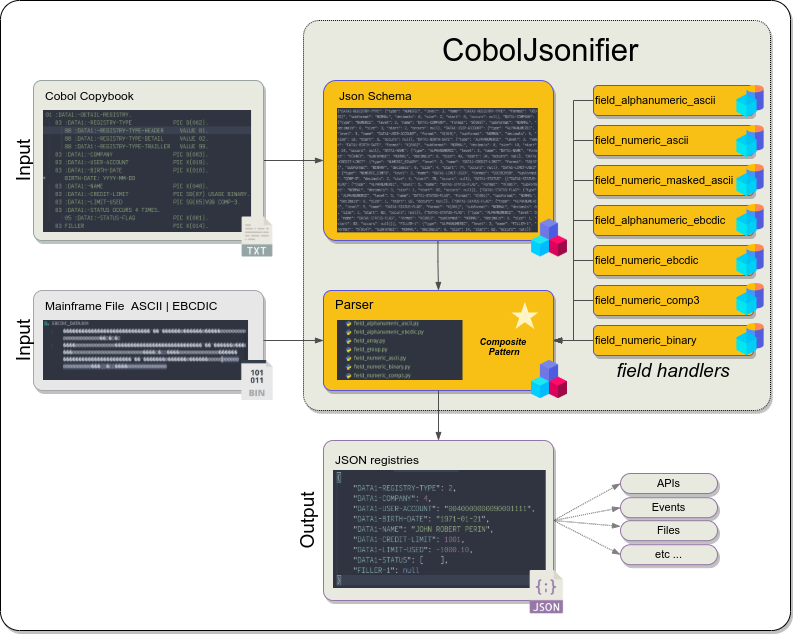
This package allows to receive data files from mainframe in ebcdic format and parse it into json based on the cobol copybook schema.
The motivator for that was the necessity to transfer and process some data files from Mainframe on cloud in a easy way for cloud systems.
The main idea here is to convert files from Mainframe that was generated by cobol programs using copybooks into json's registry format.
Cobol copybooks are like data schemas for raw positional files.
To use the package you need:
-
Extract a cobol copybook structure to generate a python dictionary. This dictionary contains objects neededs to build the parser.
-
Build a Parser based on the previous copybook's struture extracted.The parser contains python objects that will handle each kind of data field in the Mainframe's file. That file could be eater EBCDI or ASCII.
Note:
Types such as:Binary(BINARY, COMP),COMP3,Numeric Signed( S9(n) ) are supported in EBCDIC type and needs to be transfer in binary mode from Mainframe.
ASCII mode suports formats likePIC 9(n),PIC X(n)and MaskedPIC +99999.99. These formats can be converted from EBCDIC to ASCII when transfered by FTP, Connect Dirct or other tools from mainframe to cloud or another platform.
These data lines parsed into json could be used to create events, call rest apis and what else you can imagine.
Take a look at that package on pypi.org
Installing the pagacke.
pip install coboljsonifierUsing the package.
import simplejson
from coboljsonifier.copybookextractor import CopybookExtractor
from coboljsonifier.parser import Parser
from coboljsonifier.config.parser_type_enum import ParseType
...
# Extracting copybook structure
dict_structure = CopybookExtractor(bookfname).dict_book_structure
# Building a Parser
parser = Parser(dict_structure, ParseType.BINARY_EBCDIC).build()
...
# Parsing the data
parser.parse(data)
# Getting the result (it is an dict type)
dictvalue = parser.value
# Showing the result as Json
print(simplejson.dumps(dictvalue))The result will be like that:
{"DATA1-REGISTRY-TYPE": 2, "DATA1-COMPANY": 4, "DATA1-USER-ACCOUNT": "0040000000090001111", "DATA1-BIRTH-DATE": "1971-01-21", "DATA1-NAME": "JOHN ROBERT PERIN", "DATA1-CREDIT-LIMIT": 1001, "DATA1-LIMIT-USED": -1000.10, "DATA1-STATUS": [{"DATA1-STATUS-FLAG": "1"}, {"DATA1-STATUS-FLAG": "2"}, {"DATA1-STATUS-FLAG": "3"}, {"DATA1-STATUS-FLAG": "4"}], "FILLER-1": null}Use the script examples/prepare_test.py to generate files that will be used by test scripts.
Files generated:
EBCDIC_BOOK.cob&EBCDIC_DATA.binASCII_BOOK.cob&ASCII_DATA.bin
After that you can use scripts examples/ascii_parser_test.py and examples/ebcdid_parser_test.py to see how the coboljsonifier package works.
More details in examples/README.md.
-
To save in json formats is necessary to use
simplejsonpackage. It's to keep compatibility ofDecimalpakage that is used to handle monetary values. -
The common
jsonlibrary has incompatibility with Decimal values -
Install
simplejsonjust runningpip install simplejson. -
Use
simplejsonthe same way ofjson.Ex.
install simplejson as json
It will keep compatibility with the main functionalities.
$ python -m venv venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
Unit Tests:
# Note: Run the tests from main folter of the project
# Ex.: cd cobol-copybook.jsonifier/
# Running only the unittest
$ python -m unittest discover
# Checking test coveraging
$ coverage run -m unittest discover
$ coverage report -m
$ coverage htmlTable of types treated by CobolJsonifier
=======================================================================================
TYPES CLASSES EBCDIC ASCII
=======================================================================================
-[Empty]--------------------------------------------------------------------------
1) Empty Content Fieldempty yes yes
-[Numeric Types without signal]---------------------------------------------------
2) 9 FieldSimpleNumeric yes yes
3) 9V99 FieldSimpleNumericDecimals1 yes yes
4) 9V9(2) FieldSimpleNumericDecimals2 yes yes
5) 9(12) FieldSimpleNumeric1 yes yes
6) 9(12)V99 FieldSimpleNumeric1Decimals1 yes yes
7) 9(12)V9(2) FieldSimpleNumeric1Decimals2 yes yes
-[Numeric Types with signal]------------------------------------------------------
8) S9(12) [BINARY/COMP3] FieldSignalNumeric1 yes no
9) S9(12)V99 [BINARY/COMP3] FieldSignalNumeric1Decimals1 yes no
10) S9(12)V9(2) [BINARY/COMP3] FieldSignalNumeric1Decimals2 yes no
10) S9(12)V [BINARY/COMP3] FieldSignalNumeric1Decimals3 yes no
-[Masked Numeric Types]-----------------------------------------------------------
A01) +99999999999999.99 FieldNumericMasked1 no yes
-99999999999999.99
+99999999999999
+ZZZZZZZZZZZZZ9.99
-ZZZZZZZZZZZZZ9.99 (Note: These are just
ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ.ZZ some examples)
99999999999999999
-[Alphabetic]---------------------------------------------------------------------
A02) A(12) FieldAlphabetic yes yes
-[Alphanumeric]-------------------------------------------------------------------
A03) X(12) FieldAlphanumeric yes yes
-[Undefined]----------------------------------------------------------------------
11) None of the above FieldUndefined yes yes
>>>>>>> 7aefd72956e3c26456327dcd222723a04a115bf3
=======================================================================================