WARNING: This extension is experimental and should not be used in a production environment. It is intended solely to demonstrate the capability of extending a CLI tool using OpenAI.
This project is an extension for the Azure CLI that allows you to use natural language prompts to run Azure CLI commands. It uses Azure OpenAI to determine the most likely Azure CLI command to run based upon the prompt you provide.
The latest Azure CLI documentation is used to create embeddings for each Azure CLI command. These embeddings are then stored in Azure Cognitive Search and used for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to determine the most up to date syntax for the command you wish to execute.
This project is built using Microsoft Semantic Kernel, which allows for easy integration with a range of services. For more information on the open source project, see the GitHub repository
To install and use the Copilot extension you will need the following:
- An Azure subscription
- The Azure CLI installed
- Python 3.9 or later installed
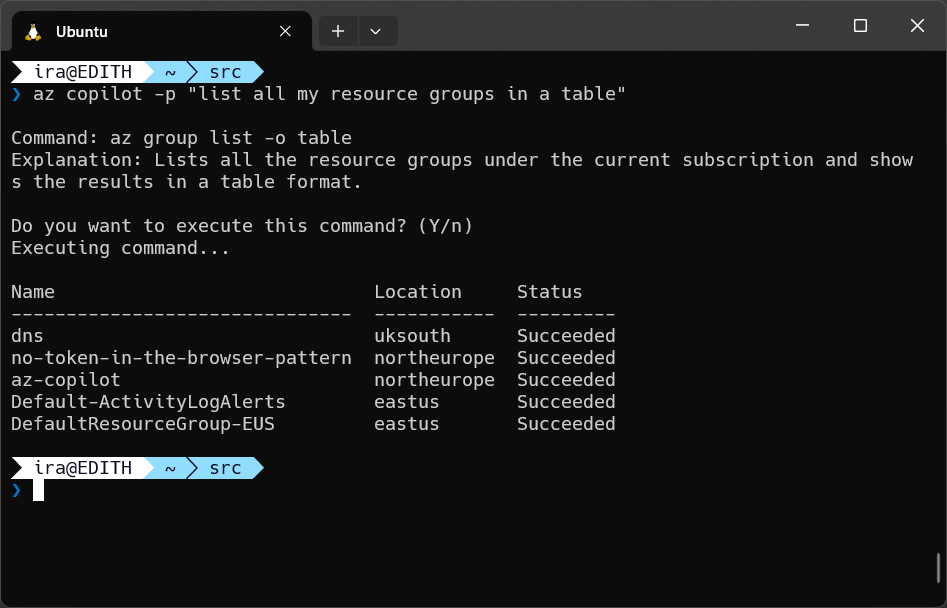
To use the Copilot simply use the command az copilot --prompt "your command prompt here". This will invoke the call to determine the most likely Azure CLI command to run based on the prompt you provide.
The Azure CLI command will then be presented to you and you can choose to run it or not by pressing y or return confirm execution. This confirmation step can be overridden by setting the global configuration setting autorun = true, or at a single command level adding the option --autorun or -a which will override the global setting, such as: az copilot --prompt "list all my resource groups in a table" -a.
WARNING: Care should be taken with autorun functionality as any commands usually requiring confirmation, such as deletion of resources, will auto confirm the action being performed.
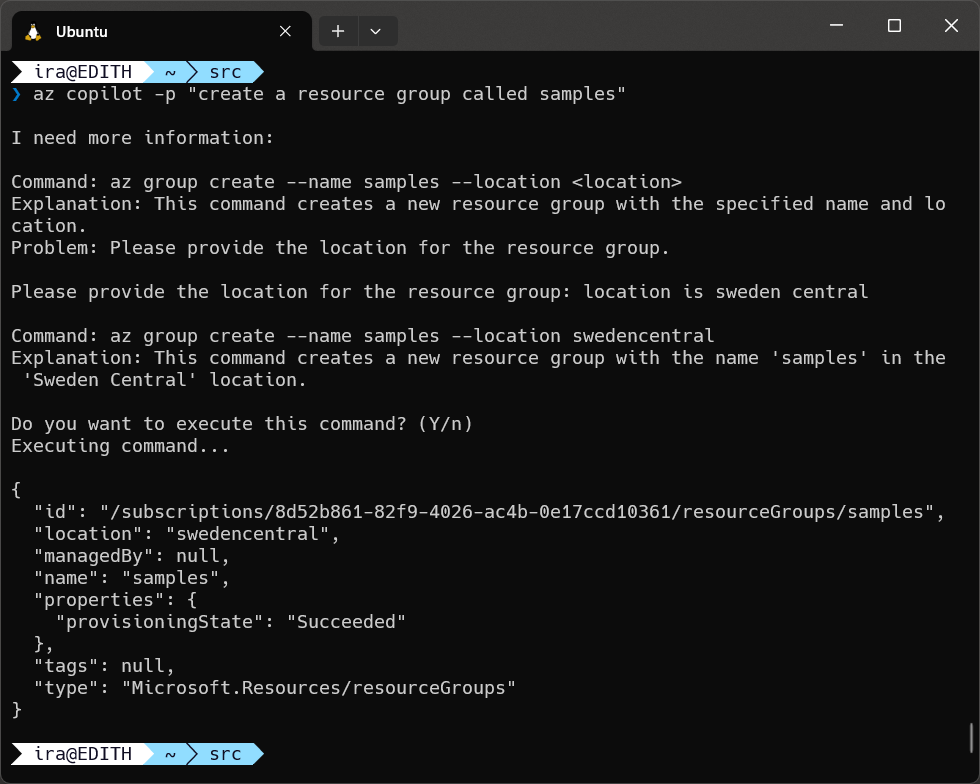
If the Copilot determines that additional information is required to execute the command, such as missing parameters, it will prompt you for the missing information. You should also use plain English commands for these conversations. You can drop out of the conversation at any time by entering quit or q.
When first installed Retrieval Augmented Generation is disabled by default. This is to ensure the relevant Azure Cognitive Search service has been setup, populated, and configured first.
Without RAG, the Copilot will only use the Azure OpenAI model to determine the most likely Azure CLI command to run based on the prompt you provide. Given this model was trained around September 2021, it means that updates made to the Azure CLI since then will not be reflected in this model.
By creating embeddings from the most recent version of the documentation, the Copilot will be able to use RAG to additionally search the embeddings and better determine the most up to date syntax for the command you wish to execute.
Once the embeddings have been generated it is recommended to enable the use of RAG. To enable RAG, use the command az copilot config set --use-rag true.
Two additional configuration options are available for RAG. These are:
--search-relevance-threshold- The relevance threshold for the search results.--search-result-count- The number of search results to return.
These settings are given default values when the Copilot extension is installed. These are:
--search-relevance-threshold 0.85--search-result-count 7
If you wish to change these values, you can do so using the command az copilot config set. Special consideration should be given to the number of results returned, as the more results returned, the larger the resulting prompt being sent to the OpenAI service will be, which could then break the token limit. Changing the relevance threshold change the accuracy of the results returned and hence the quality of the command generated.
The Copilot extension has several global configuration options that can be used to control the flow of the command. These are:
--autorun- Automatically run the command when ready--show-command- Show the Azure CLI command to be run--enable-logging- Enable logging of the command flow
These are all boolean settings that can be set using the command az copilot config set.
Default settings are:
--autorun false--show-command true--enable-logging false.
If you are comfortable with the Copilot extension and want to speed up the flow, you can set --autorun true. This will automatically run the command when ready.
Note: Any command that requires a confirmation will also be automatically confirmed. This is to ensure the command flow is not interrupted, but can be dangerous if you are not sure what the command will do, or if it is destructive such as with a delete command.
To get up and running with the Copilot extension, you will need to complete several steps. In order these are:
- Clone this repository so the deployment scripts are available locally
- Deploy required Azure OpenAI and Azure Cognitive Services resources
- Install the Azure CLI Copilot extension
- Set the configuration values as output by the infrastructure deployment
- Run the extraction script to create up to date embeddings from the Azure CLI documentation
Each of these steps is detailed below.
To deploy the required Azure OpenAI and Azure Cognitive Search resources, you can use the deployment script in the infrastructure directory. To make it simpler, a makefile has been provided to run the deployment script. From a bash terminal, run the following command:
make deploy-infraWhen the deployment is complete, the output will be displayed in the terminal. This will include the API keys and endpoints for the Azure OpenAI and Azure Cognitive Search resources. These values will be required when setting the configuration for the Copilot extension.
By default resources created are named az-copilot-<unique id>. This unique name is generated from a hash of the current Azure Subscription ID and the current timestamp. If you wish to change this, it can be done by editing the variable in the deploy.sh file.
Likewise the location for deployment is set in the deploy.sh file. By default this is set to uksouth. If you wish to change this, it can also be done by editing the deploy.sh file.
The Azure OpenAI service will also deploy two models. The first is the completion model, which is gpt-35-turbo-16k and the second is the embedding model, which is text-embedding-ada-002.
When deploying Azure OpenAI services, ensure you have enough quota available in the specified region for your subscription, or the deployment will fail.
The Copilot extension is available as a Python wheel file and can be downloaded from the releases page. The extension can also be installed using the az extension add command by referencing the hosted release directly.
To install the extension directly, check out the releases page, determine the version number of the latest release and run the following command specifying the version number in the filename:
az extension add --source https://github.com/irarainey/az-copilot/releases/download/latest/copilot-0.1.16-py3-none-any.whl --yesYou can check the version of the extension you have installed by running the following command:
az copilot versionTo unstall the extension, simply run the extension az extension remove command:
az extension remove --name copilotThe Copilot extension requires several configuration options to be set. All configuration options are stored in a local configuration file stored in the root of your user profile directory, in a directory named .az-copilot. The configuration file is named config.json.
If the configuration file does not exist, it will be created when you run any extension command or the embedding deployment script.
You can edit this file manually, or use the az copilot config set command to set the configuration options. All parameters are optional. You can set a single value, or all values at once.
For information on the options available, run the command az copilot config set --help
This will display the following table of options:
Command
az copilot config set
Arguments
--autorun -a : Global boolean value to autorun the command when ready.
--completion-name -cn : The Azure OpenAI completion model deployment name.
--embedding-name -en : The Azure OpenAI embedding model deployment name.
--enable-logging -l : Boolean value to enable or disable logging.
--openai-api-key -ok : The Azure OpenAI API key.
--openai-endpoint -oe : The Azure OpenAI endpoint.
--search-api-key -sk : The Azure Cognitive Search API key.
--search-endpoint -se : The Azure Cognitive Search endpoint.
--search-index-name -si : The Azure Cognitive Search index name.
--search-relevance-threshold -st : The Azure Cognitive Search relevance threshold.
--search-result-count -sc : The Azure Cognitive Search result count.
--search-vector-size -sv : The Azure Cognitive Search vector size.
--show-command -s : Boolean value to show or hide commands.
--use-rag -r : Boolean value to enable or disable RAG.
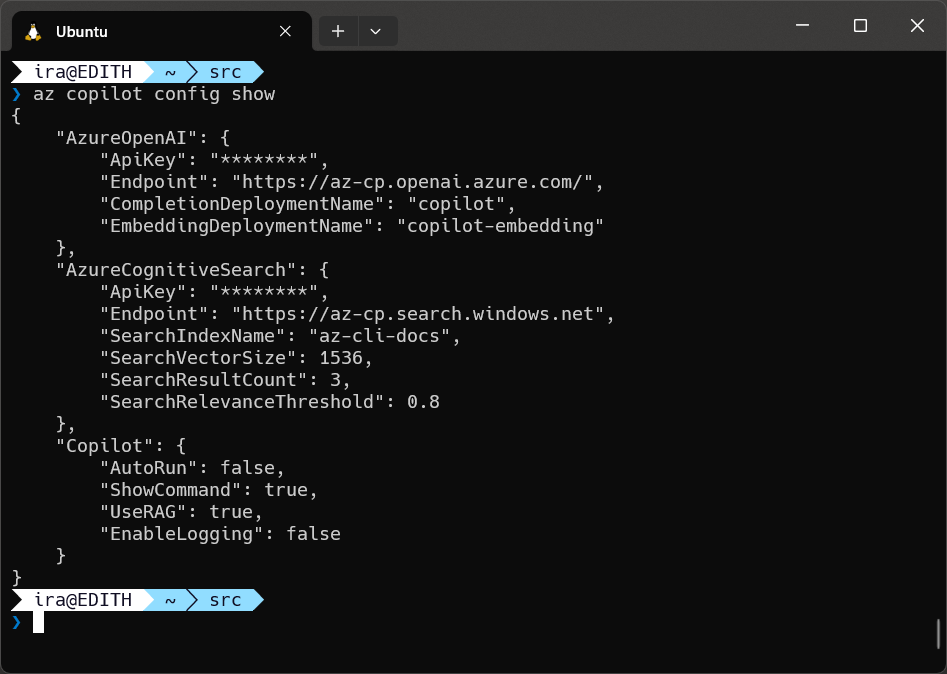
Additionally you can use the command az copilot config show to display the current configuration options.
NOTE: For security reasons API keys are not displayed in the output.
Once the Azure OpenAI and Azure Cognitive Search resources have been deployed, the Copilot extension has been installed, and the configuration values have been set, you can generate the embeddings required for RAG.
To generate the embeddings, you can use the main.py script in the extract directory. To make it simpler, a makefile has been provided to run the extraction script. From a bash terminal, run the following command:
make extract-docsThis script will extract the latest version of the Azure CLI documentation directly from the GitHub repository in YAML format, parse it, and create the embeddings required for RAG. A single text document is created locally in the extract/docs directory for each command, which includes syntax and examples, and is then used to create the embeddings which are stored in Azure Cognitive Search.
At the time of writing there are just over 11,000 Azure CLI commands. Depending upon the speed of your connection, this process will take around one hour to complete. The script will output the progress to the terminal.
This extension is heavily based on an internal project created for the Microsoft Global Hackathon 2023 called Azure Maestro. A huge thanks to the entire team for their hard work that made this possible. The epic team members were: Marc van Duyn, Amin Espinoza, Arjen Kroezen, Hayward van Biljon, Jaya Kumar, Michael Collier, Nuno Silva, Sherryl Manalo, and myself.