生活中,垃圾随处可见。道路需要清洁工人们辛苦打扫,并根据一定的规则进行垃圾种类划分。本项目旨在简化该项同类任务中的前置任务,即垃圾智能检测定位与识别,然后搭载小车实现垃圾分类收集。后期,只需要将收集好的垃圾,交于清洁工人们进行简单再分类即可完成路面等地方的垃圾收集分类工作。
主要框架:
-
垃圾检测功能: 采用深度学习的目标检测算法实现,PaddleDetection开发 -
硬件部署: 采用树莓派4B,32位操作系统,PaddleLite开发 -
硬件协同: (小车结构在该项目的展示中,暂未说明)
其它资料:
PPDet: PaddleDetection为飞桨的官方目标检测套件,可以实现众多目标检测模型的训练。
本项目,基于PPDet开发PPyolo_r18vd模型作为垃圾检测项目的深度学习模型,以期望获得视觉中出现的指定垃圾的类别以及相对位置信息,从而辅助目标检测模型的应用。
本项目实现的模型,最终落地于
垃圾分拣车上——实现垃圾的定位与识别检测,从而进行定位抓取与垃圾识别。
项目所需模型要求如下:
-
模型运行速度
-
模型漏检率优先
-
模型检测识别精度
预期模型选择: -- ppyolo_r18_vd -- , -- ppyolo_tiny --
| 模型 | 精度(all:%) | 帧率(s) | 漏检率 | 训练成本 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppyolo_tiny | 0.5_mAP:95+ | 3-5 | 一般 | 低 |
| ppyolo_r18_vd | 0.5_mAP:97+ | 1.4-1.6 | 较低 | 低 |
数据集格式: COCO/VOC都有尝试, 本项目选用COCO介绍。
感兴趣的小伙伴可以观看一个PPDet使用(说明)视频: PPDet简单使用教程
声音有些小,可能需要带耳机食用~,还望谅解
本项目基于套件本身进行开发,因此需要导入套件包——已挂载到本项目,可直接使用
如本地,请自行下载
# -oq 静默解压
!unzip -oq data/data99077/PaddleDetection-release-2.1.zip
!mv PaddleDetection-release-2.1 PaddleDetection为方便模型开发训练,因此直接解压到套件中的
dataset目录下,并新建diy_coco来保存
数据集目录:
-
PaddleDetection-
dataset-
diy_coco-
Train-
Annotations: 包含coco格式的标注json文件 -
Images: 训练图片
-
-
Eval-
Annotations: 包含coco格式的标注json文件 -
Images: 验证/评估图片
-
-
-
-
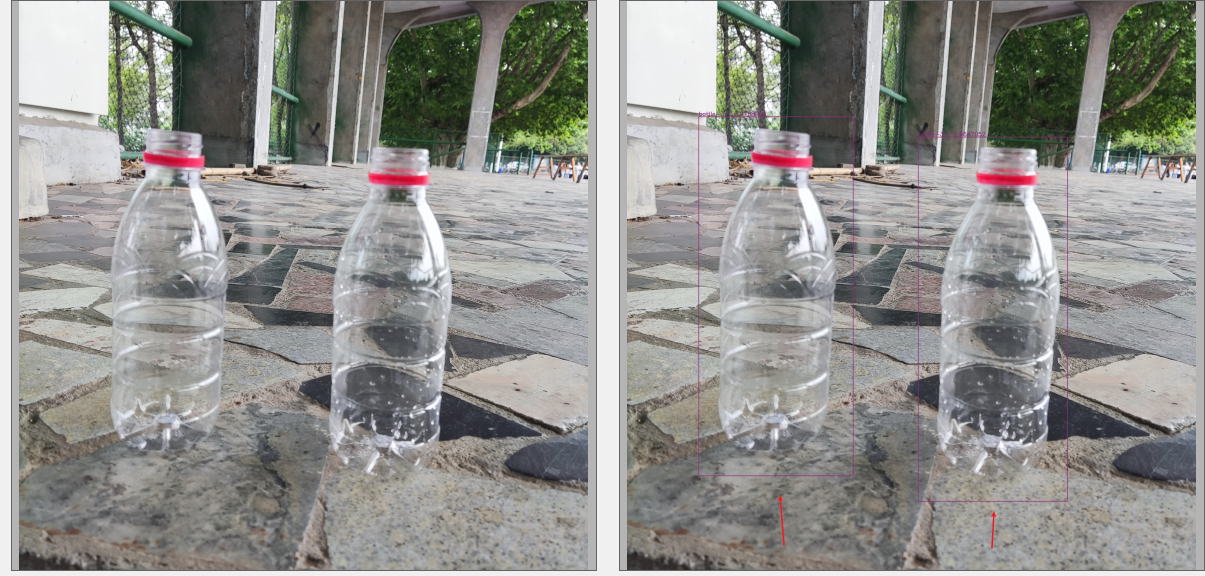
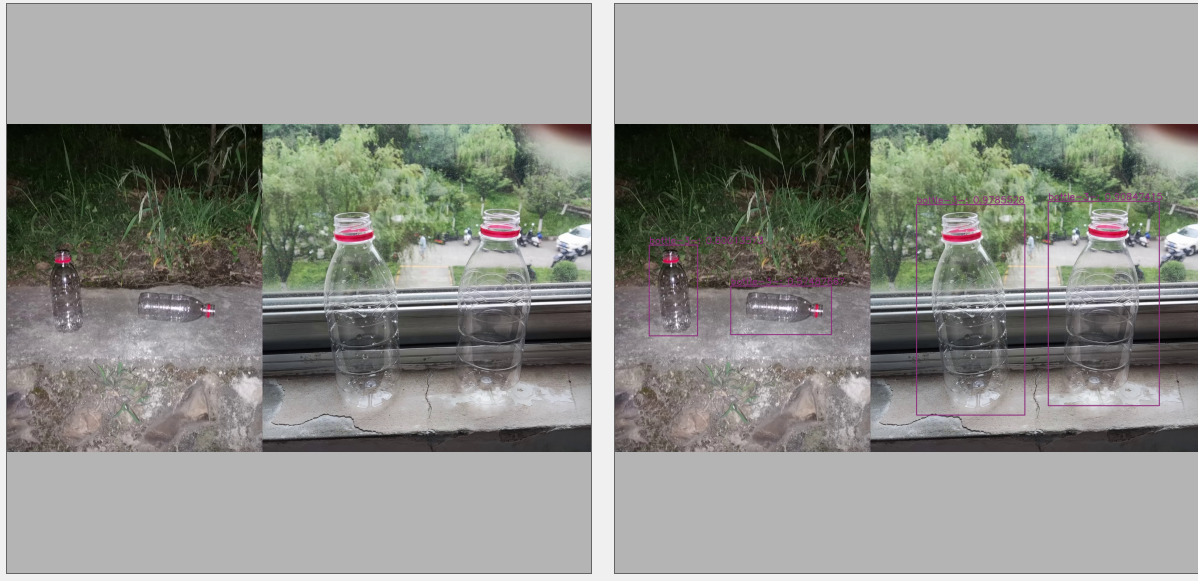
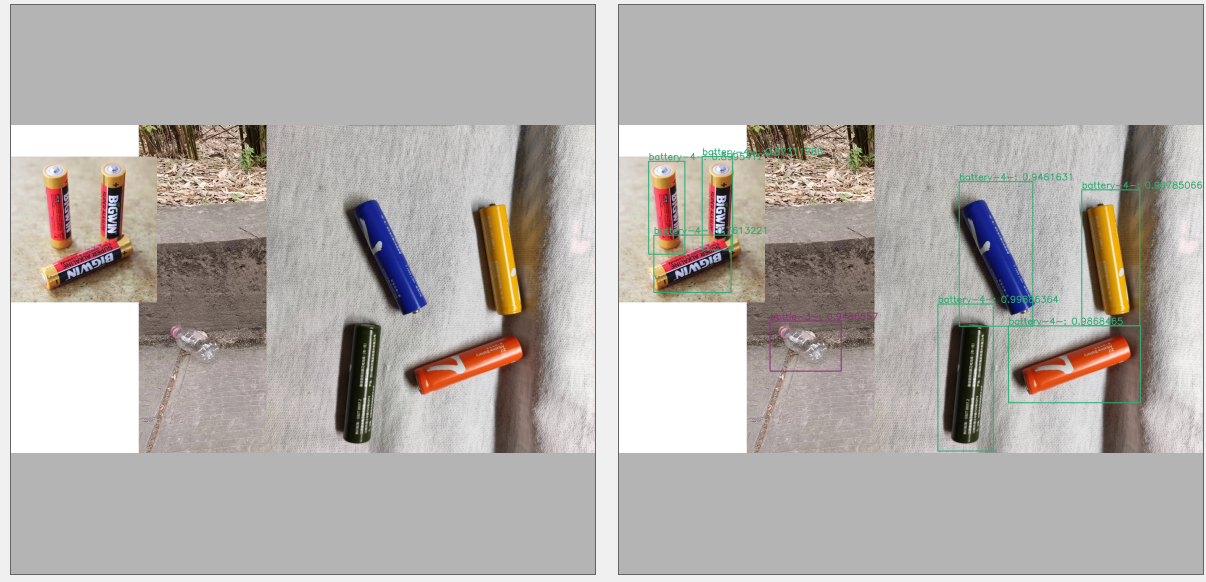
部分数据标注展示:
!unzip -oq data/data101886/rubish_det.zip -d PaddleDetection/dataset/diy_coco主要是补充下载pycocotool,这对解析coco数据格式的标注提供很大的帮助
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleDetection
!pip install -r requirements.txt在训练开始前,现在训练数据上,生成一个符合待拟合数据的
anchor,这将对模型学习合适的特征提供帮助,同时也能更好的框选预测物体的位置!
仅限于需要
预置anchor的模型
不过,再开始生成anchor前,需要先配置好数据集的加载。
因为,本项目的数据格式为coco,因此选择路径: PaddleDetection/configs/datasets下的coco_detection.yml文件进行修改,使其加载本项目垃圾检测数据!
修改如下:
metric: COCO
# 修改num_classes为垃圾分类的数量
num_classes: 5
TrainDataset:
!COCODataSet
# 2.再配置图片路径 -- 指向Images文件夹
image_dir: Images
# 3.最后配置标注文件的路径 -- 指向Annotations下的json文件
anno_path: Annotations/train.json
# 1.先配置数据集目录 -- 先指向Train文件夹
dataset_dir: dataset/diy_coco/Train
# end: 这里不同改
data_fields: ['image', 'gt_bbox', 'gt_class', 'is_crowd']
EvalDataset:
!COCODataSet
image_dir: Images
anno_path: Annotations/val.json
# 1. 指向另一个文件夹,用于验证评估,其它同上
dataset_dir: dataset/diy_coco/Eval
TestDataset:
!ImageFolder
# 这里的标注配置,设置为验证的json即可
anno_path: Annotations/val.json
已经有了配置好的数据加载yml文件,接下来就可以选模型了。
这里选用PaddleDetection/configs/ppyolo下的ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml作为项目要训练的模型。
以上完成了数据加载的配置以及模型的选择之后,我们就可进行预置anchor的自动生成了!
生成的大致流程:
-
启动时,调用
模型yml进入参数配置,获取数据集加载的yml信息 -
生成时,利用数据集中的
所有已有标注信息进行anchor的kmeans聚类生成一个anchor集合 -
使用时,将生成的anchor收集起来,然后替换模型yml中所有出现anchor列表的地方`即可
# -n: 模型中需要的anchor数量, r18只需要6个
# -s: 生成anchor集合,适用于多大的输入尺寸 —— 会自动生成指定大小下的anchor集合
# -c: 指定使用这些anchor的模型yml
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleDetection
!python tools/anchor_cluster.py -n 6 -s 320 -c configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml替换anchor的地方,对于r18而言有以下两个地方:
configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml,configs/ppyolo/_base_/ppyolo_r18vd.yml
ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml中的修改如下(模型yml):
- Gt2YoloTarget:
anchor_masks: [[3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
# 替换anchor列表为生成的anchor即可
anchors: [[48, 36], [43, 66], [89, 60], [60, 102], [105, 124], [165, 163]]
downsample_ratios: [32, 16]
ppyolo_r18vd.yml中的修改如下(模型结构yml):
YOLOv3Head:
anchor_masks: [[3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
# 替换anchor列表为生成的anchor即可
anchors: [[48, 36], [43, 66], [89, 60], [60, 102], [105, 124], [165, 163]]
loss: YOLOv3Loss
create_anchors_list = [[59, 45], [54, 82], [112, 74], [75, 127], [131, 154], [206, 204]]对于r18而言,训练参数的修改只需要在
configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml中修改即可
主要参数修改如下:
TrainReader:
sample_transforms:
...
batch_transforms:
- BatchRandomResize:
# 原始大小的list对应输入大小为520的预测,现改为320之后,简要修改的这个区间
# 修改注意事项,每个大小都是32的倍数
target_size: [224, 256, 288, 320, 352, 384, 416, 448]
...
- Gt2YoloTarget:
anchor_masks: [[3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
# 替换为生成的anchor
anchors: [[48, 36], [43, 66], [89, 60], [60, 102], [105, 124], [165, 163]]
downsample_ratios: [32, 16]
# 根据数据集情况,适当修改即可: 8/16/24/32/48
batch_size: 32
mixup_epoch: 500
shuffle: true
EvalReader:
sample_transforms:
- Decode: {}
# target_size改为320
- Resize: {target_size: [320, 320], keep_ratio: False, interp: 2}
...
TestReader:
inputs_def:
# 改为320
image_shape: [3, 320, 320]
sample_transforms:
- Decode: {}
# 改为320
- Resize: {target_size: [320, 320], keep_ratio: False, interp: 2}
...
LearningRate:
# 原4卡下训练参数,除以4,用于单卡训练
# 0.004 / 4 == 0.001
base_lr: 0.001
...
%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleDetection
!python tools/train.py\
-c configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml\
--eval\
--use_vdl True[08/14 21:03:03] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [196] [20/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.773786 loss_wh: 0.697323 loss_iou: 2.933347 loss_obj: 3.114668 loss_cls: 0.885066 loss: 8.543031 eta: 0:27:02 batch_cost: 0.4652 data_cost: 0.2992 ips: 68.7832 images/s
[08/14 21:03:12] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [196] [40/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.757029 loss_wh: 0.656280 loss_iou: 2.774072 loss_obj: 3.072931 loss_cls: 0.949183 loss: 8.486620 eta: 0:26:52 batch_cost: 0.4206 data_cost: 0.2787 ips: 76.0866 images/s
[08/14 21:03:17] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [197] [ 0/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.758142 loss_wh: 0.664071 loss_iou: 2.743285 loss_obj: 3.071552 loss_cls: 1.033830 loss: 8.424139 eta: 0:26:50 batch_cost: 0.4621 data_cost: 0.3208 ips: 69.2533 images/s
[08/14 21:03:26] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [197] [20/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.736949 loss_wh: 0.639424 loss_iou: 2.764338 loss_obj: 3.022928 loss_cls: 1.026918 loss: 8.329489 eta: 0:26:40 batch_cost: 0.4258 data_cost: 0.2777 ips: 75.1583 images/s
[08/14 21:03:36] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [197] [40/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.728324 loss_wh: 0.671651 loss_iou: 2.920363 loss_obj: 3.044627 loss_cls: 0.976078 loss: 8.474413 eta: 0:26:30 batch_cost: 0.4600 data_cost: 0.3220 ips: 69.5716 images/s
[08/14 21:03:40] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [198] [ 0/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.748800 loss_wh: 0.663416 loss_iou: 2.903050 loss_obj: 3.142794 loss_cls: 0.995665 loss: 8.490379 eta: 0:26:27 batch_cost: 0.5249 data_cost: 0.3624 ips: 60.9593 images/s
[08/14 21:03:50] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [198] [20/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.804090 loss_wh: 0.638163 loss_iou: 2.821011 loss_obj: 3.293034 loss_cls: 0.950222 loss: 8.611068 eta: 0:26:17 batch_cost: 0.4455 data_cost: 0.2798 ips: 71.8259 images/s
[08/14 21:03:59] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [198] [40/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.729478 loss_wh: 0.671696 loss_iou: 2.855099 loss_obj: 2.954676 loss_cls: 1.013126 loss: 8.109439 eta: 0:26:08 batch_cost: 0.4445 data_cost: 0.3092 ips: 71.9917 images/s
[08/14 21:04:04] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [199] [ 0/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.729086 loss_wh: 0.640540 loss_iou: 2.748984 loss_obj: 3.005687 loss_cls: 0.877229 loss: 7.902369 eta: 0:26:05 batch_cost: 0.5034 data_cost: 0.3502 ips: 63.5677 images/s
[08/14 21:04:14] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [199] [20/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.763439 loss_wh: 0.640906 loss_iou: 2.689836 loss_obj: 3.238860 loss_cls: 0.929343 loss: 8.205533 eta: 0:25:56 batch_cost: 0.4675 data_cost: 0.2824 ips: 68.4485 images/s
[08/14 21:04:24] ppdet.engine INFO: Epoch: [199] [40/46] learning_rate: 0.000100 loss_xy: 0.757755 loss_wh: 0.720121 loss_iou: 2.960909 loss_obj: 3.277584 loss_cls: 0.926977 loss: 8.504792 eta: 0:25:46 batch_cost: 0.4711 data_cost: 0.3046 ips: 67.9259 images/s
[08/14 21:04:27] ppdet.utils.checkpoint INFO: Save checkpoint: output/ppyolo_r18vd_coco
[08/14 21:04:27] ppdet.engine INFO: Eval iter: 0
[08/14 21:04:32] ppdet.metrics.metrics INFO: The bbox result is saved to bbox.json.
loading annotations into memory...
Done (t=0.01s)
creating index...
index created!
[08/14 21:04:32] ppdet.metrics.coco_utils INFO: Start evaluate...
Loading and preparing results...
DONE (t=0.12s)
creating index...
index created!
Running per image evaluation...
Evaluate annotation type *bbox*
DONE (t=1.27s).
Accumulating evaluation results...
DONE (t=0.19s).
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.667
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.960
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.836
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.771
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = -1.000
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = -1.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.394
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.764
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.776
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.776
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = -1.000
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = -1.000
[08/14 21:04:34] ppdet.engine INFO: Total sample number: 636, averge FPS: 141.8495250691227
[08/14 21:04:34] ppdet.engine INFO: Best test bbox ap is 0.668.
将模型导出,并且打开--export_serving_model,适当能够生成__model__, __params__格式的模型与参数文件
导出前, 需要前往:
configs/ppyolo/_base_/ppyolo_r18vd.yml这个模型结构文件中,注释掉:pretrain_weights后再进行模型导出
如下:
architecture: YOLOv3
# pretrain_weights: https://paddledet.bj.bcebos.com/models/pretrained/ResNet18_vd_pretrained.pdparams
norm_type: sync_bn
use_ema: true
ema_decay: 0.9998
# --export_serving_model指令下需要下载该依赖
!pip install paddle-serving-client%cd /home/aistudio/PaddleDetection
!python tools/export_model.py\
-c configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml\
-o weights='output/ppyolo_r18vd_coco/best_model'\
--output_dir '/home/aistudio/export_model'\
--export_serving_model True/home/aistudio/PaddleDetection
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/__init__.py:107: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
from collections import MutableMapping
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/rcsetup.py:20: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
from collections import Iterable, Mapping
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/colors.py:53: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
from collections import Sized
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle/tensor/creation.py:125: DeprecationWarning: `np.object` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `object`. To silence this warning, use `object` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe.
Deprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations
if data.dtype == np.object:
[08/14 21:29:42] ppdet.utils.checkpoint INFO: Finish loading model weights: output/ppyolo_r18vd_coco/best_model.pdparams
[08/14 21:29:42] ppdet.engine INFO: Export inference config file to /home/aistudio/export_model/ppyolo_r18vd_coco/infer_cfg.yml
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle/fluid/layers/utils.py:77: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
return (isinstance(seq, collections.Sequence) and
W0814 21:29:44.067077 20354 device_context.cc:404] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 10.1, Runtime API Version: 10.1
W0814 21:29:44.067139 20354 device_context.cc:422] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
[08/14 21:29:47] ppdet.engine INFO: Export model and saved in /home/aistudio/export_model/ppyolo_r18vd_coco
# 查看输出结构
!tree /home/aistudio/export_model -L 3/home/aistudio/export_model
└── ppyolo_r18vd_coco
├── infer_cfg.yml
├── model.pdiparams
├── model.pdiparams.info
├── model.pdmodel
├── serving_client
│ ├── serving_client_conf.prototxt
│ └── serving_client_conf.stream.prototxt
└── serving_server
├── __model__
├── __params__
├── serving_server_conf.prototxt
└── serving_server_conf.stream.prototxt
3 directories, 10 files
部署需要的内容主要有以下两种
-
*.pdmodel+*.pdiparams -
__model__+__params__
其它可能需要的资料(PaddleLite不直接用,可以作为加载的一些预处理参数的参考):
infer_cfg.yml,serving_server_conf.prototxt
利用可视化推理验收模型效果:
- 图片推理效果
- 视频推理效果
本项目训练的模型部署到树莓派4B上进行应用,能够实现较为快速准确的垃圾检测!
部署说明与部分检测(展示为tiny的效果, 部署代码通用)的效果可以观看视频: 树莓派部署教程与效果展示
部分效果:
如果使用32位的操作系统,可以直接使用我编译好的whl(使用与Python3)
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pmULmyNokBcG7EQz2gKWCg
提取码:plit
下载好后,上传到树莓派即可 —— 推荐使用vnc远程服务的文件传递功能。
安装指令:
python3 -m pip install whl_path
-
- 先使用
paddlelite包中的opt这个API实现模型的转换,获取nb格式的文件
- 先使用
-
- 然后使用以下代码进行
模型加载即可进行模型推理
- 然后使用以下代码进行
主要处理
-
加载模型,并输出加载时间
__init__ -
获取输入数据,配置模型输入 --
get_input_img- 注意不同模型的输入数据
-
获取绘制好框的图像结果 --
get_output_img
部署代码,来自个人项目: PPYolo-Tiny树莓派部署实践(一)
一些注意事项,可以看下面的代码,可以观看树莓派部署视频!
from paddlelite.lite import *
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from time import time
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageFont
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageEnhance
class PPYOLO_Detector(object):
def __init__(self, nb_path = None, # nb路径
label_list = None, # 类别list
input_size = [320, 320], # 输入图像大小
img_means = [0., 0., 0.], # 图片归一化均值
img_stds = [0., 0., 0.], # 图片归一化方差
threshold = 0.1, # 预测阈值
num_thread = 1, # ARM CPU工作线程数
work_power_mode = PowerMode.LITE_POWER_NO_BIND # ARM CPU工作模式
):
# 验证必要的参数格式
assert nb_path is not None, \
"Please make sure the model_nb_path has inputed!(now, nb_path is None.)"
assert len(input_size) == 2, \
"Please make sure the input_shape length is 2, but now its length is {0}".format(len(input_size))
assert len(img_means) == 3, \
"Please make sure the image_means shape is [3], but now get image_means' shape is [{0}]".format(len(img_means))
assert len(img_stds) == 3, \
"Please make sure the image_stds shape is [3], but now get image_stds' shape is [{0}]".format(len(img_stds))
assert len([i for i in img_stds if i <= 0]) < 1, \
"Please make sure the image_stds data is more than 0., but now get image_stds' data exists less than or equal 0."
assert threshold > 0. and threshold < 1., \
"Please make sure the threshold value > 0. and < 1., but now get its value is {0}".format(threshold)
assert num_thread > 0 and num_thread <= 4, \
"Please make sure the num_thread value > 1 and <= 4., but now get its value is {0}".format(num_thread)
assert work_power_mode in [PowerMode.LITE_POWER_HIGH, PowerMode.LITE_POWER_LOW,
PowerMode.LITE_POWER_FULL, PowerMode.LITE_POWER_NO_BIND,
PowerMode.LITE_POWER_RAND_HIGH,
PowerMode.LITE_POWER_RAND_LOW], \
"Please make sure the work_power_mode is allowed , which is in \
[PowerMode.LITE_POWER_HIGH, PowerMode.LITE_POWER_LOW, \
PowerMode.LITE_POWER_FULL, PowerMode.LITE_POWER_NO_BIND, \
PowerMode.LITE_POWER_RAND_HIGH, \
PowerMode.LITE_POWER_RAND_LOW], \
but now get its value is {0}"
# 模型nb文件路径
self.model_path = nb_path
# ARM CPU工作线程数
self.num_thread = num_thread
# ARM CPU工作模式
self.power_mode = work_power_mode
# 预测显示阈值
self.threshold = threshold
# 预测输入图像大小
self.input_size = input_size
# 图片归一化参数
# 均值
self.img_means = img_means
# 方差
self.img_stds = img_stds
# 预测类别list
self.label_list = label_list
# 预测类别数
self.num_class = len(label_list) if (label_list is not None) and isinstance(label_list, list) else 1
# 类别框颜色map
self.box_color_map = self.random_colormap()
# 记录模型加载参数的开始时间
self.prepare_time = self.runtime()
# 配置预测
self.config = MobileConfig()
# 设置模型路径
self.config.set_model_from_file(nb_path)
# 设置线程数
self.config.set_threads(num_thread)
# 设置工作模式
self.config.set_power_mode(work_power_mode)
# 构建预测器
self.predictor = create_paddle_predictor(self.config)
# 模型加载参数的总时间花销
self.prepare_time = self.runtime() - self.prepare_time
print("The Prepare Model Has Cost: {0:.4f} s".format(self.prepare_time))
def get_input_img(self, input_img):
'''输入预测图片
input_img: 图片路径或者np.ndarray图像数据 - [h, w, c]
'''
assert isinstance(input_img, str) or isinstance(input_img, np.ndarray), \
"Please enter input is Image Path or numpy.ndarray, but get ({0}) ".format(input_img)
# 装载图像到预测器上的开始时间
self.load_img_time = self.runtime()
if isinstance(input_img, str):
# 读取图片路径下的图像数据
self.input_img = Image.open(input_img)
elif isinstance(input_img, np.ndarray):
# 读取ndarray数据下的图像数据
self.input_img = Image.fromarray(input_img)
# 获取图片原始高宽 : h,w
self.input_shape = np.asarray(self.input_img).shape[:-1]
# 重置图片大小为指定的输入大小
input_data = self.input_img.resize(self.input_size, Image.BILINEAR)
# 转制图像shape为预测指定shape
input_data = np.array(input_data).transpose(2, 0, 1).reshape([1, 3] + self.input_size).astype('float32')
# 将图像数据进行归一化
input_data = self.normlize(input_data)
self.scale_factor = [1., 1.] # [1., 1.]
# 配置输入tensor
# 输入[[shape, shape]]的图片大小
self.input_tensor0 = self.predictor.get_input(0)
self.input_tensor0.from_numpy(np.asarray([self.input_size], dtype=np.int32))
# 输入[1, 3, shape, shape]的归一化后的图片数据
self.input_tensor1 = self.predictor.get_input(1)
self.input_tensor1.from_numpy(input_data)
# 输入模型处理图像大小与实际图像大小的比例
self.input_tensor2 = self.predictor.get_input(2)
self.input_tensor2.from_numpy(np.asarray(self.scale_factor, dtype=np.int32))
# 装载图像到预测器上的总时间花销
self.load_img_time = self.runtime() - self.load_img_time
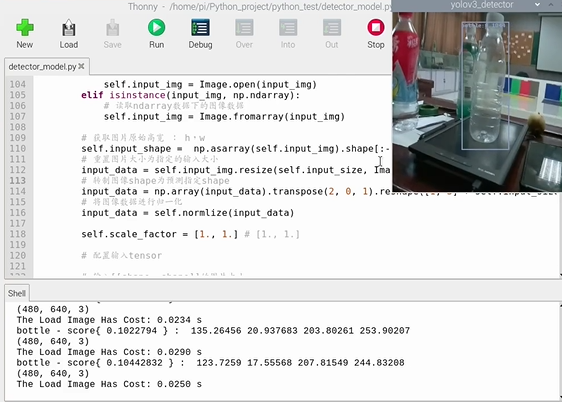
print("The Load Image Has Cost: {0:.4f} s".format(self.load_img_time))
def get_output_img(self, num_bbox=1):
'''获取输出标注图片
num_bbox: 最大标注个数
'''
# 预测器开始预测的时间
self.predict_time = self.runtime()
# 根据get_input_img的图像进行预测
self.predictor.run()
# 获取输出预测bbox结果
self.output_tensor = self.predictor.get_output(0)
# 转化为numpy格式
output_bboxes = self.output_tensor.numpy()
# 根据阈值进行筛选,大于等于阈值的保留
output_bboxes = output_bboxes[output_bboxes[:, 1] >= self.threshold]
# 根据预测结果进行框绘制,返回绘制完成的图片
self.output_img = self.load_bbox(output_bboxes, num_bbox)
# 预测器预测的总时间花销
self.predict_time = self.runtime() - self.predict_time
print("The Predict Image Has Cost: {0:.4f} s".format(self.predict_time))
return self.output_img
def normlize(self, input_img):
'''数据归一化
input_img: 图像数据--numpy.ndarray
'''
# 对RGB通道进行均值-方差的归一化
input_img[0, 0] = (input_img[0, 0] / 255. - self.img_means[0]) / self.img_stds[0]
input_img[0, 1] = (input_img[0, 1] / 255. - self.img_means[1]) / self.img_stds[1]
input_img[0, 2] = (input_img[0, 2] / 255. - self.img_means[2]) / self.img_stds[2]
return input_img
def load_bbox(self, input_bboxs, num_bbox):
'''根据预测框在原始图片上绘制框体,并标注
input_bboxs: 预测框
num_bbox: 允许的标注个数
'''
# 创建间绘图参数:[cls_id, score, x1, y1, x2, y2]
self.draw_bboxs = [0] * 6
# 绘图器 -- 根据get_input_img的输入图像
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(self.input_img)
# 根据最大标注个数进行实际标注个数的确定
# input_bboxs.shape[0]: 表示预测到的有效框个数
if len(input_bboxs) != 0: # 存在有效框时
num_bbox = input_bboxs.shape[0] if num_bbox > input_bboxs.shape[0] else num_bbox
else:
num_bbox = 0 # 没有有效框,直接不标注
# 遍历框体,并进行标注
for i in range(num_bbox):
# 类别信息
self.draw_bboxs[0] = input_bboxs[i][0]
# 类别得分
self.draw_bboxs[1] = input_bboxs[i][1]
print(self.label_list[int(self.draw_bboxs[0])], '- score{', self.draw_bboxs[1], "} : ", input_bboxs[i][2], input_bboxs[i][3], input_bboxs[i][4], input_bboxs[i][5])
# 框体左上角坐标
# max(min(input_bboxs[i][2] / self.input_size[0], 1.), 0.):保证当前预测坐标始终在图像内(比例,0.-1.)
# max(min(input_bboxs[i][2] / self.input_size[0], 1.), 0.) * self.input_shape[1]: 直接预测得到的坐标
# min(max(min(input_bboxs[i][2] / self.input_size[0], 1.), 0.) * self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[1]):保证坐标在图像内(h, w)
self.draw_bboxs[2] = min(max(min(input_bboxs[i][2] / self.input_size[0], 1.), 0.) * self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[1])
self.draw_bboxs[3] = min(max(min(input_bboxs[i][3] / self.input_size[1], 1.), 0.) * self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[0])
# 框体右下角坐标
self.draw_bboxs[4] = min(max(min(input_bboxs[i][4] / self.input_size[0], 1.), 0.) * self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[1])
self.draw_bboxs[5] = min(max(min(input_bboxs[i][5] / self.input_size[1], 1.), 0.) * self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[0])
# print(self.draw_bboxs[2], self.draw_bboxs[3], self.draw_bboxs[4], self.draw_bboxs[5])
# 绘制框体
# self.box_color_map[int(self.draw_bboxs[i][0])]: 对应类别的框颜色
draw.rectangle(((self.draw_bboxs[2], self.draw_bboxs[3]),
(self.draw_bboxs[4], self.draw_bboxs[5])),
outline = tuple(self.box_color_map[int(self.draw_bboxs[0])]),
width =2)
# 框体位置写上类别和得分信息
draw.text((self.draw_bboxs[2], self.draw_bboxs[3]+1),
"{0}:{1:.4f}".format(self.label_list[int(self.draw_bboxs[0])], self.draw_bboxs[1]),
tuple(self.box_color_map[int(self.draw_bboxs[0])]))
# 返回标注好的图像数据
return np.asarray(self.input_img)
def random_colormap(self):
'''获取与类别数量等量的color_map
'''
np.random.seed(2021)
color_map = [[np.random.randint(20, 255),
np.random.randint(64, 200),
np.random.randint(128, 255)]
for i in range(self.num_class)]
return color_map
def runtime(self):
'''返回当前计时
'''
return time()有需要的小伙伴,可以搭载串口通信,实现树莓派与单片机直接的通信哦!
def test():
model_path = "/home/pi/test/ppyolo_tiny/ppyolo_tiny.nb" # 模型参数nb文件 -- 自行修改
img_path = "/home/pi/Desktop/citrus_0005.jpg" # 自己的预测图像
label_list = ['bottle', 'battery', 'cup', 'paper', 'citrus'] # 类别list
input_size = [224, 224] # 输入图像大小
img_means = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] # 图片归一化均值
img_stds = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225] # 图片归一化方差
threshold = 0.1 # 预测阈值
num_thread = 2 # ARM CPU工作线程数
work_mode = PowerMode.LITE_POWER_NO_BIND # ARM CPU工作模式
max_bbox_num = 1 # 每帧最多标注数
# 创建预测器
detector = PPYOLO_Detector(
nb_path = model_path,
label_list = label_list,
input_size = input_size,
img_means = img_means,
img_stds = img_stds,
threshold = threshold,
num_thread = num_thread,
work_power_mode = PowerMode.LITE_POWER_NO_BIND
)
img = plt.imread(img_path)
img = cv.resize(img,(320, 320)) # 与训练时配置的大小一致
detector.get_input_img(img) # 输入图片数据
img = detector.get_output_img(num_bbox = max_bbox_num) # 得到预测输出后绘制了框的图像
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()请看传送门: 树莓派部署教程与效果展示
一直以来,人工智能落地都是一个工业界的热门话题。近年内,有许多优秀的检测算法出现,YOLOV4-PPYOLO-PPYOLOV2等。但在落地时,不光要考虑精度,还需要实时性——也就是考虑部署设备的算力情况。
因此,本项目就基于PPDet展开了较轻量化模型PPyolo_r18的模型训练来实现垃圾的检测分类,同时利用PaddleLite完成在树莓派端的部署,实现分拣车的视觉关键部分。
通过本项目,可以对目标检测落地提供一个可行的方案,也是基于python3的PaddleLite部署Paddle模型的一个部署实践方案。
主要收获的点如下:
-
- 数据集不大时,可以先用
大的batch_size跑1/3的轮次稳定损失下降,然后利用1/2的batch_size进行接下来的轮次训练,实现继续优化
- 数据集不大时,可以先用
-
- 数据输入大小影响着模型处理的快慢,输入图像越小,模型推理越快
-
- 部署时,根据需要可进行
量化处理``(支持INT8,INT16`),实现更快的模型加载和保存(模型体积减小).
- 部署时,根据需要可进行
姓名:蔡敬辉
学历:大三(在读)
爱好:喜欢参加一些大大小小的比赛,不限于计算机视觉——有共同爱好的小伙伴可以关注一下哦~后期会持续更新一些自制的竞赛baseline和一些竞赛经验分享
主要方向:目标检测、图像分割与图像识别
联系方式:qq:3020889729 微信:cjh3020889729
学校:西南科技大学