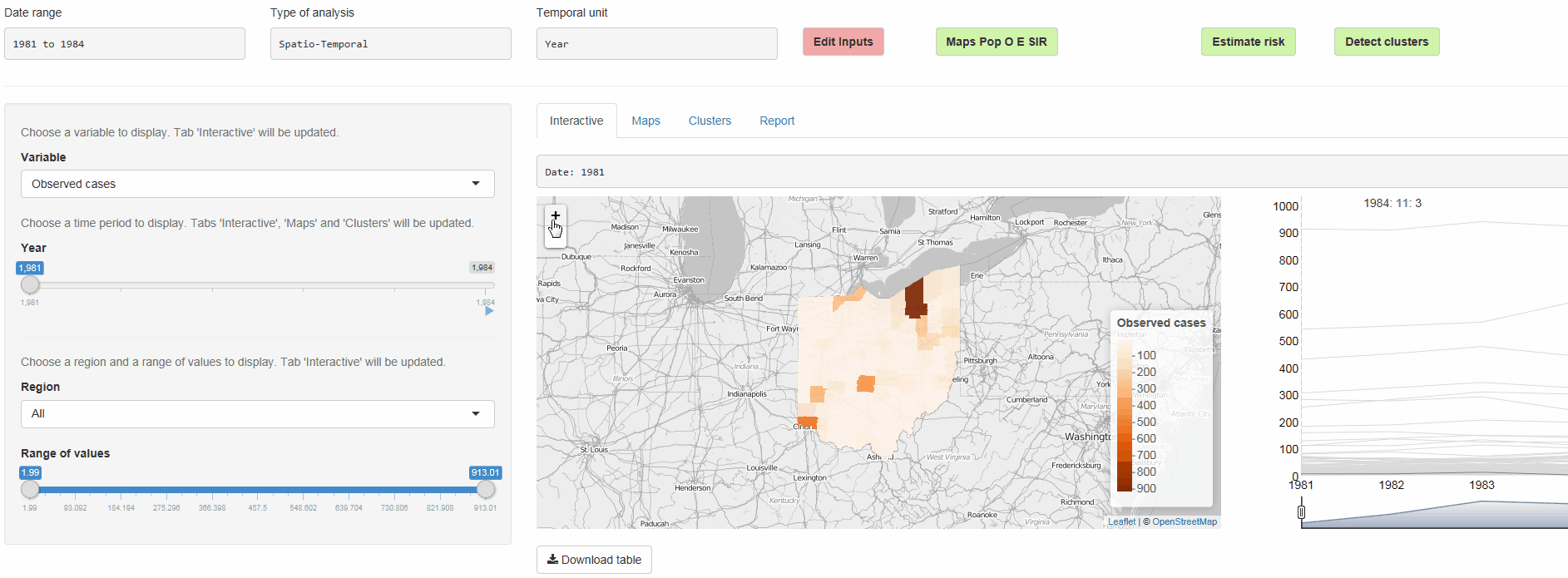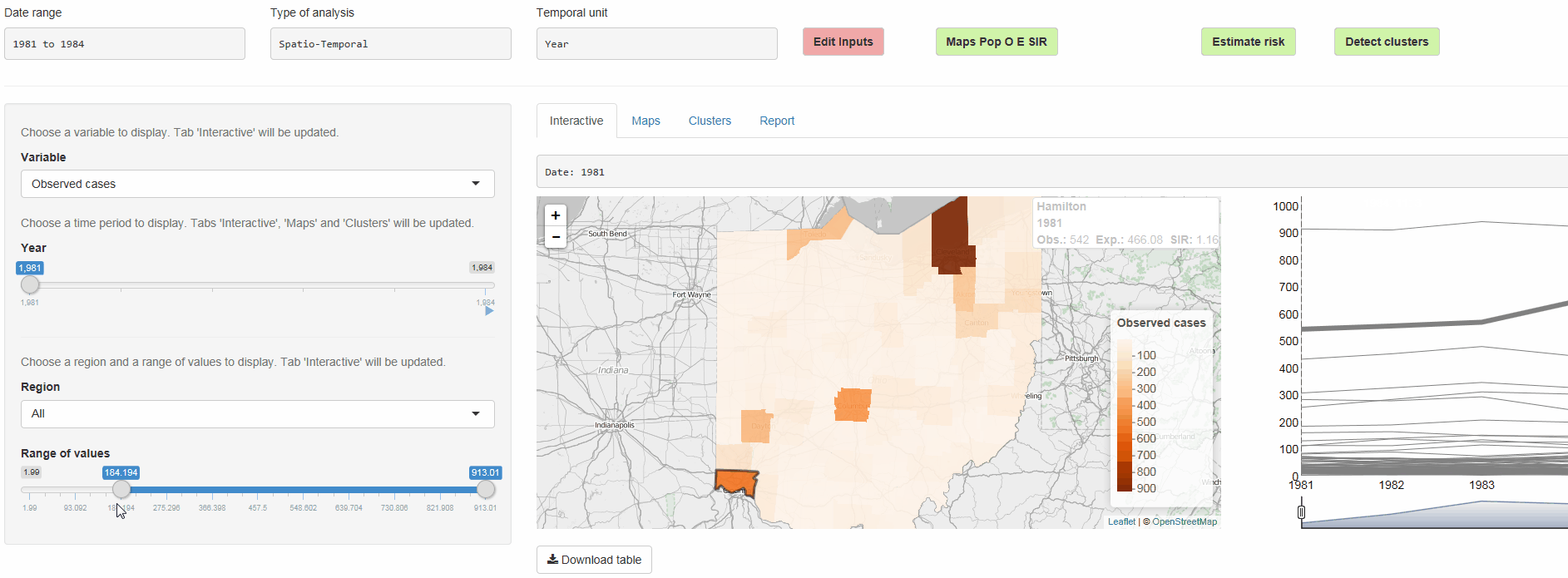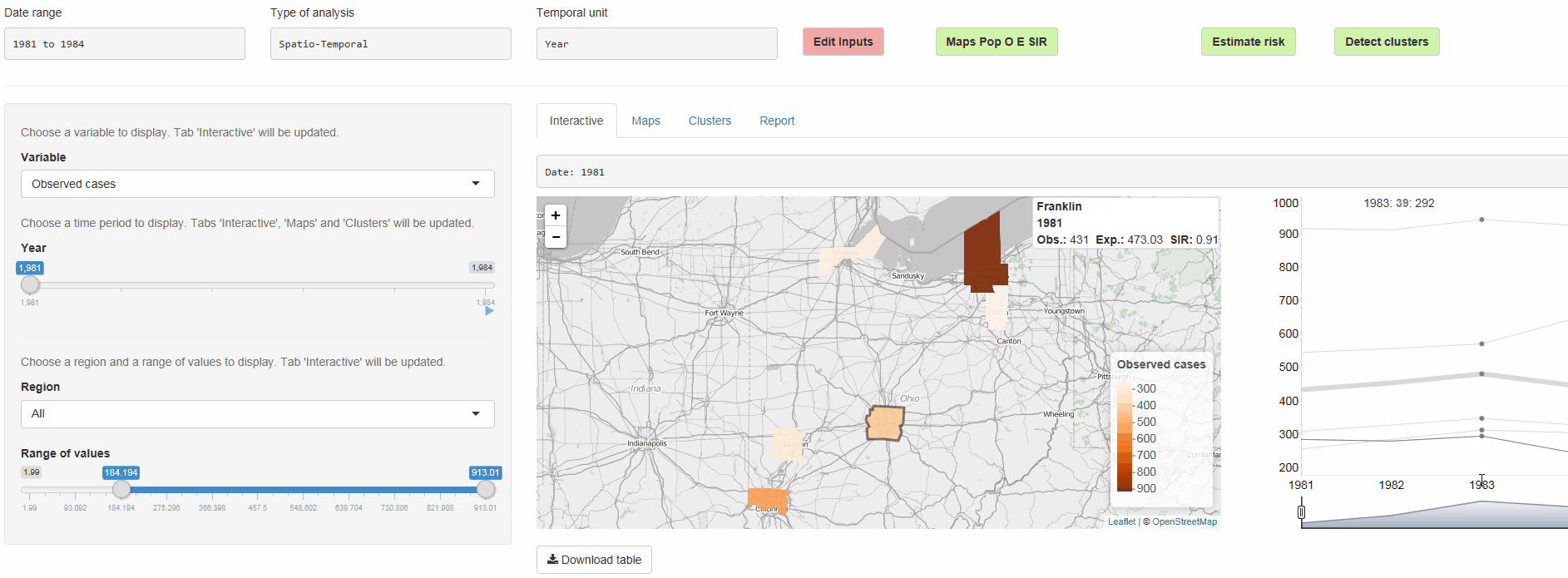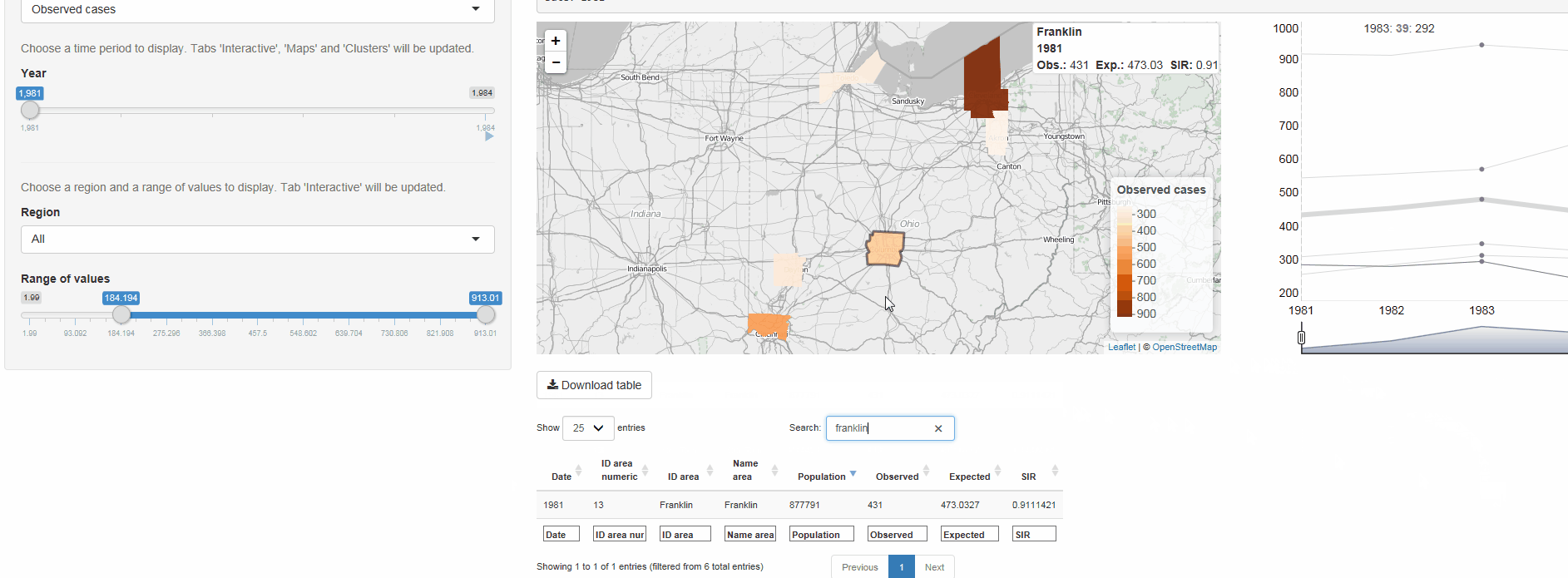
The R package SpatialEpiApp runs a Shiny web application that allows to visualize spatial and spatio-temporal disease data, estimate disease risk, and detect clusters. The application incorporates modules for
-
Disease risk estimation using Bayesian hierarchical models with INLA,
-
Detection of clusters using the scan statistics implemented in SaTScan,
-
Interactive visualizations such as maps supporting padding and zooming and tables that allow for filtering,
-
Generation of reports containing the analyses performed.
SpatialEpiApp allows user interaction and creates interactive visualizations by using the R packages Leaflet for rendering maps, dygraphs for plotting time series, and DataTables for displaying data objects. It also enables the generation of reports containing the analyses performed by using RMarkdown.
SpatialEpiApp may be useful for many researchers working in health surveillance lacking the adequate statistical and programming skills to effectively use the statistical software required to conduct the statistical analyses.
With SpatialEpiApp, we simply need to upload the map and data and then click the buttons that create the input files required, execute the software and process the output to generate tables of values and plots with the results.
This blog post, and the package vignette can be checked for more details about its use, methods and examples. Data for running examples are in https://Paula-Moraga.github.io/software
References
Moraga, P. (2017), SpatialEpiApp: A Shiny Web Application for the analysis of Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Disease Data. Spatial and Spatio-temporal Epidemiology, 23:47-57