Maslow create breaks with the tradition of CAD programs which inherit from drawing programs and instead inherits from logical languages like programing. This allows it to be a CAD program which has language like features such as importing modules, version control, and colaboration.
A 3D model within Maslow Create is composed of interconnected nodes called Atoms and Molecules. An atom is an operation you can perform on a shape (ie translate it in space). A molecule can contain any number of atoms in a configuration (ie generate a table leg). Think of Atoms as the built in functions of a programing language and molecules as the functions you create.
You can place a new atom by right clicking anywhere within the flow canvas area and entering an atom name in the search bar.
Currently Maslow Create supports the folowing atoms:
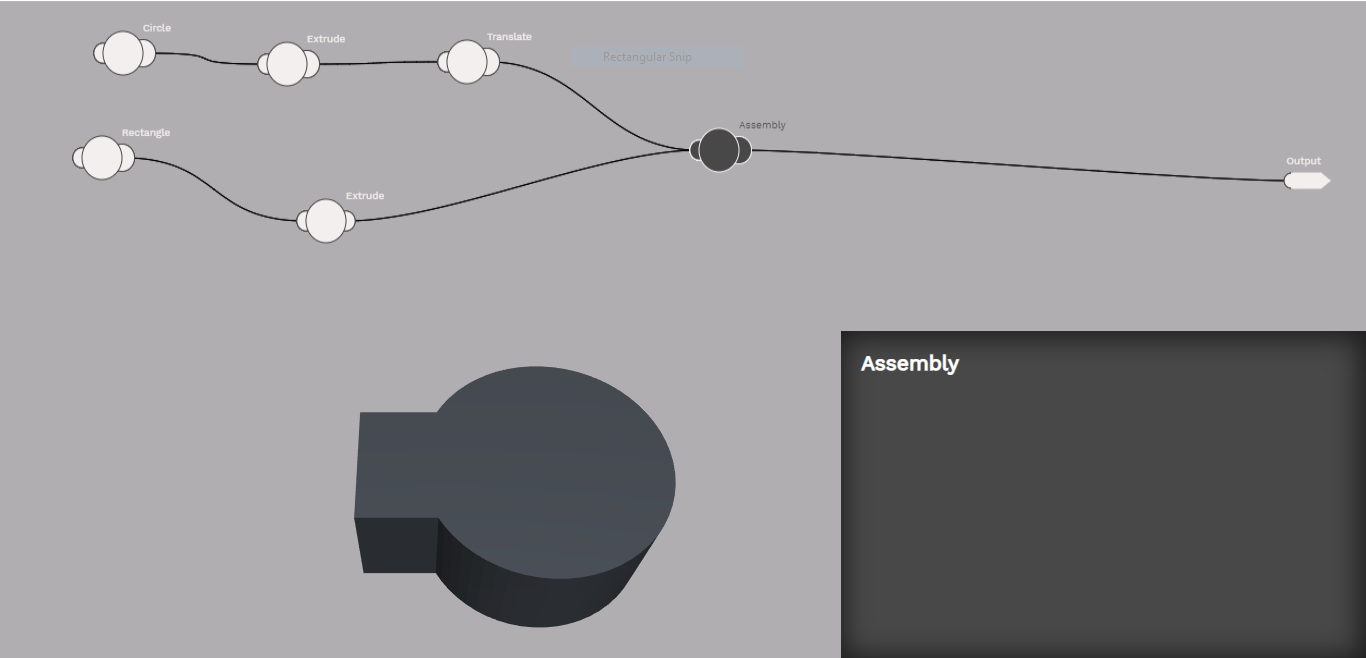
The assembly atom allows multiple shapes to be combigned into one unit called an assembly. The order in which atoms are combigned matters because where shapes intersect shapes earlier in the order subtract from shapes later in the order. For example if you have a bolt which needs to create a hole in a part you should assemble first the part and then the bolt.
The Add BOM Tag atom tags a part with a bill of materials item. This item will appear in the project bill of materials one time each time the tagged part appears in the final shape. For example if you have a table leg which needs four bolts, and the final model has four table legs the bolt will automatically appear in the final bill of materials 16 times.
{picture of tag} {picture of BOM file}
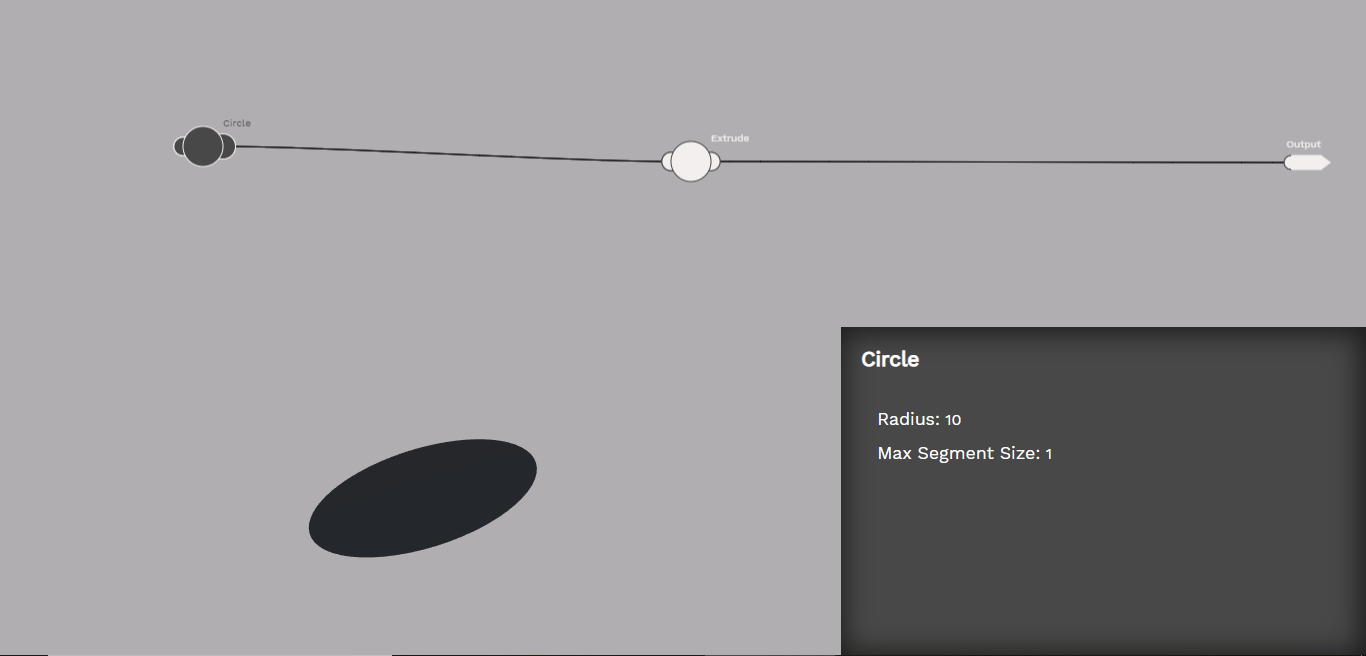
The circle atom creates a circle shape. Circle shapes are commonly extruded to create cylinders.
The code atom allows you to enter arbitrary jsxcad code. Please note that parts of this interface are likely to change in the near future.
The constant atom defines a constant number which can be used to control multiple inputs.
{picture of constant controling multiple inputs}
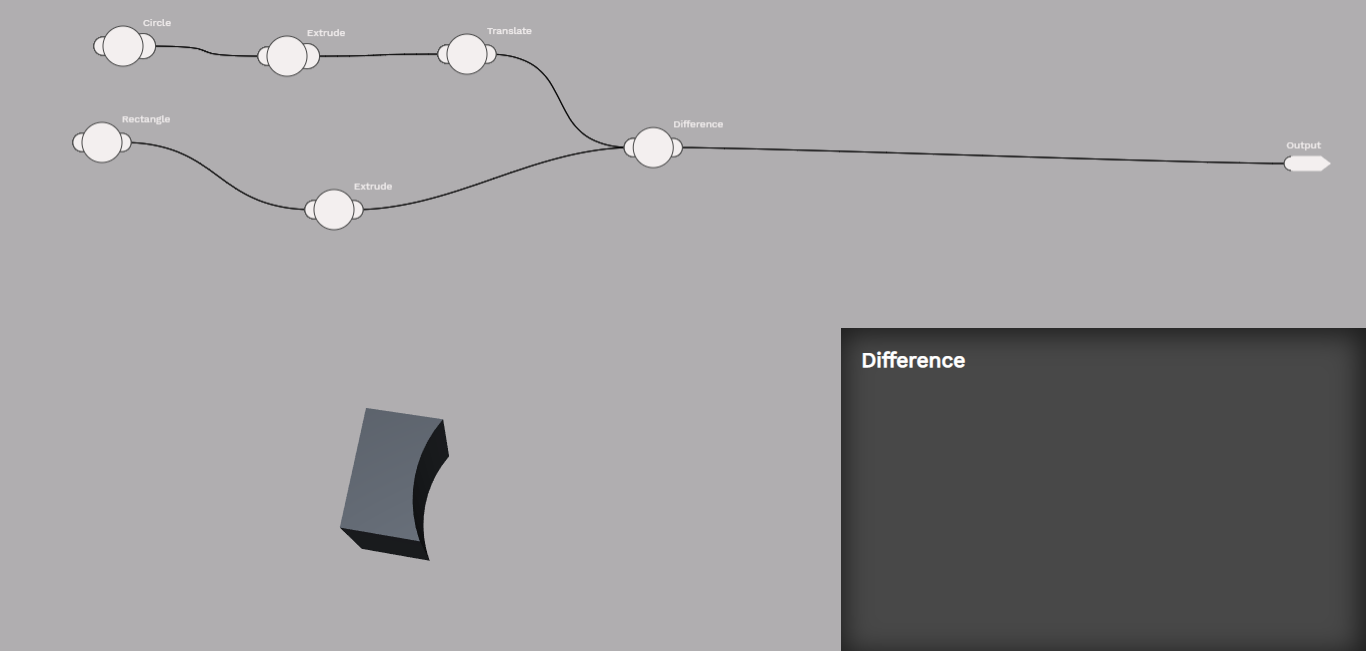
The difference atom subtracts one shape from another.
The equation Atom lets you perform basic math operations on numbers produced by constants.
{Show equation doing something}
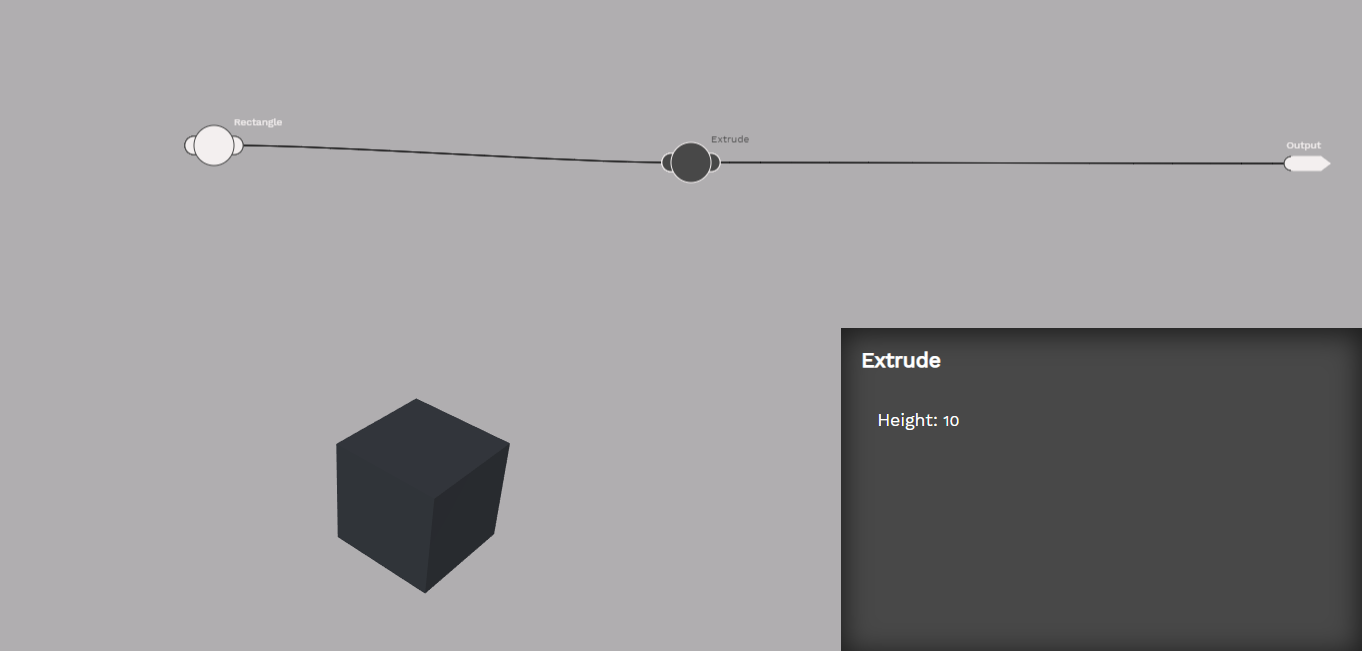
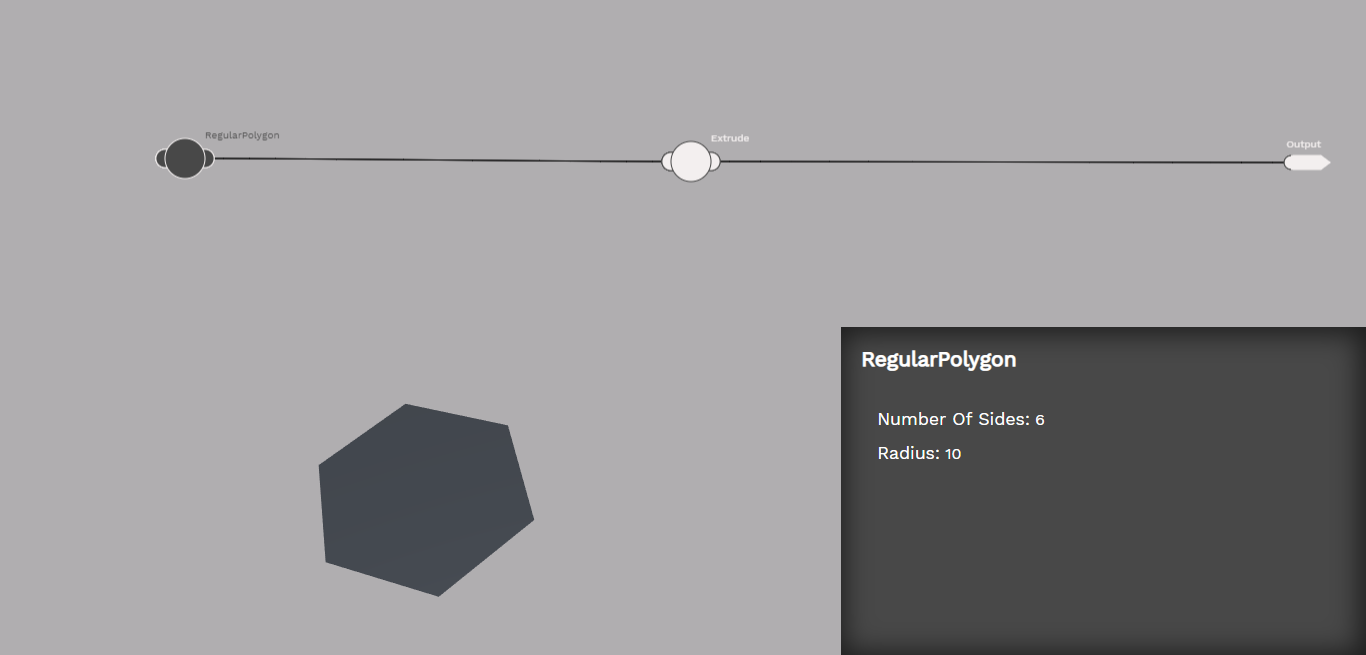
The extrude atom takes a 2D shape and makes it 3D.
The gcode atom generates gcode to cut the input shape.
The GitHub atom type is not directly available. By clicking on the GitHub tab when placing a new Atom you can search for and add any other Maslow Create project to your project.
The input atom lets you define which variables are inputs to your program. They function similar to constants, however when you share your project, the person on the other end will have the ability to change the values of the inputs. Inputs placed within a molecule will add inputs to that molecule up one level.
{picture of project being shared}
The intersection atom computes the area of intersection of two shapes and creates a new shape out of that area.
{picture of intersection}
The molecule atom can contain any number of atoms in a useful configuration. To add inputs to the molecule, place an input atom within it.
{picture of molecule}
The output atom cannot be directly placed, however each molecule has one output which cannot be delted. Connect a shape to the output of a molecule to make that shape available one level up. The output of the top level molecule is the output of the project.
The README atom provides notes to the next person reading the project. The text of the readme input is added to the readme page of the project (similar to this page you are reading now).
{Show readme atom}
The rectangle atom creates a rectangle shape. Rectangles are commonly extruded to make a 3D shape.
{show picture of rectangle}
The regular polygon atom creates a regular polygon shape. Regular polygons are regularly extruded to create a 3D shape.
The rotate atom rotates a shape along any of it's three axis.
{picture of rotate}
The scale atom scales a shape evenly in all directions.
{picture of scale}
The shrinkwrap atom combines multiple shapes into a single shape as if they had been shrinkwrapped. This is useful for creating shapes which would be dificult to create in other ways.
{picture of shrinkwrap}
The stretch atom stretches a shape along any of its axis.
{picture of stretch}
The tag atom adds a tag to a part which can be later used to retrieve that part from an assembly.
The translate atom moves a 3D shape in 3D space or a 2D shape in 2D space.
{picture of translate}
The union atom combines multiple shapes into a single shape.
{picture of union}
You can read the complete documentation at https://maslowcreate.org/documentation/
-
Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/BarbourSmith/Maslow-Create.git -
Install dependencies:
npm install -
Run webpack:
npm start
Your canvas piece should open up automatically at http://localhost:3000 and you should see 'HTML CANVAS BOILERPLATE' on hover.
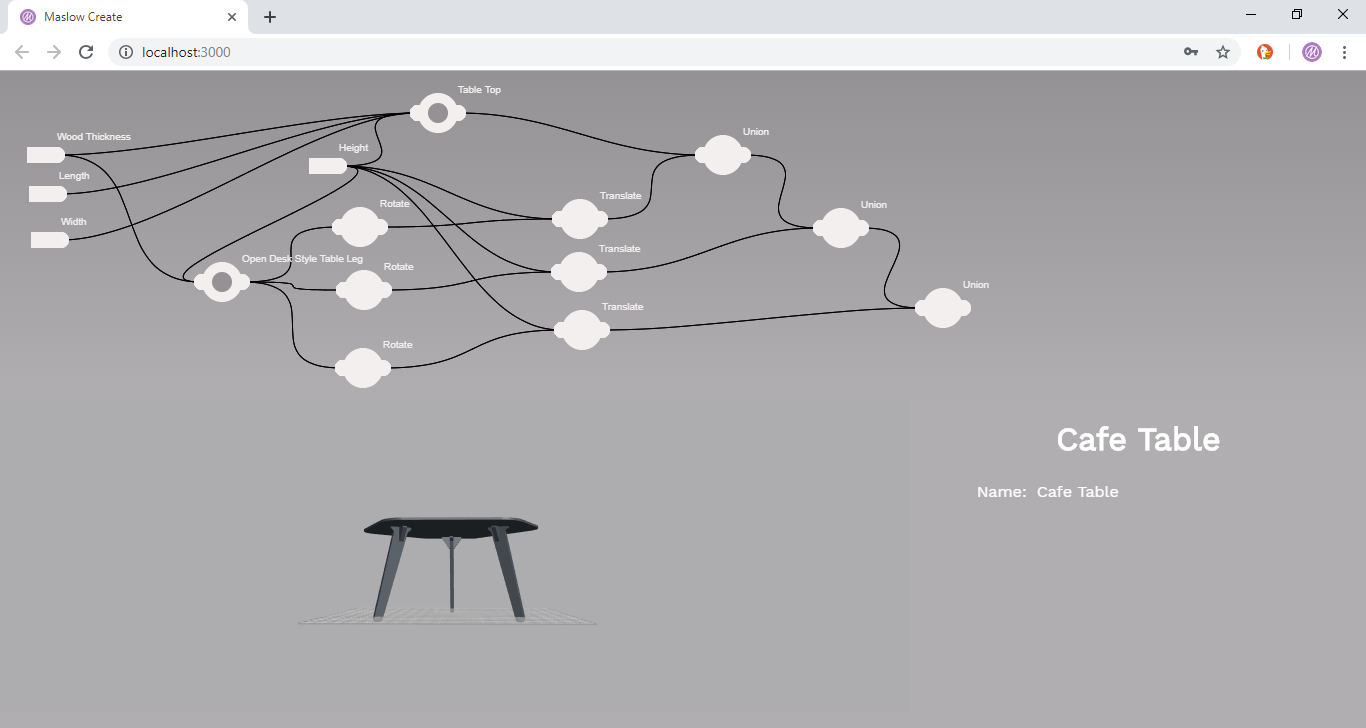
Maslow Create has three main areas of the interface. Along the top of the screen is the logical flow of the design. In the lower left is a 3D rendering of the design, and in the lower right is the side bar which displays information related to the currently selected atom. If no atom is selected, then information about the open molecule is displayed.
The logical flow of the design is composed of nodes called Atoms which are connected by connectors. Each atom has a number of attachment points where connectors can connect. Each atom type inherits from the atom class which is defined in the file /dist/js/molecules/prototypes.js. Each atom type then has it's own file which modifies the behavior of the default atom class.
The lower left 3D rendring is an instance of the JSCAD project. It is currently a hacked version of 1.x while waiting for version 2 to be released. Right now the generated code is done through string manipulation. In version 2 we will pass actual JS objects to functions.
The lower right corner of the screen is called the "Side Bar" It contains information about the currently selected atom. It is populated by that atom's "Generate Sidebar" function.