Yifan Xu, Xinhao Li, Yichun Yang, Desen Meng, Rui Huang, Limin Wang
🌟 CaReBench is a fine-grained benchmark comprising 1,000 high-quality videos with detailed human-annotated captions, including manually separated spatial and temporal descriptions for independent spatiotemporal bias evaluation.

📊 ReBias and CapST Metrics are designed specifically for retrieval and captioning tasks, providing a comprehensive evaluation framework for spatiotemporal understanding in video-language models.
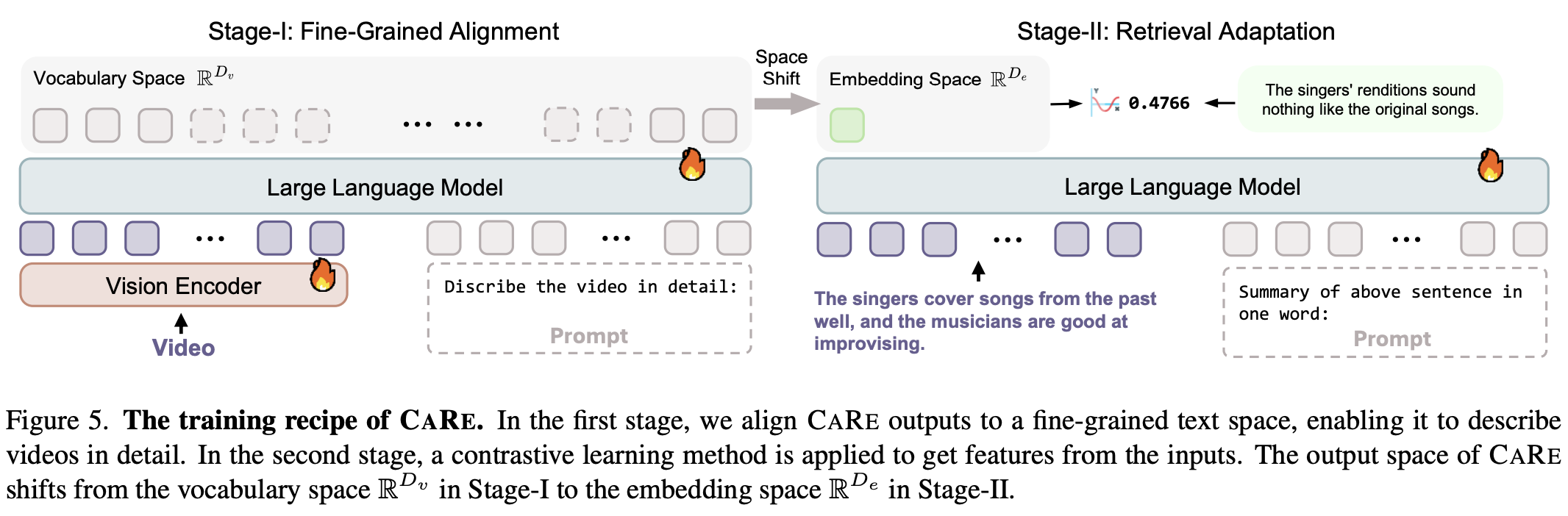
⚡ CaRe: A Unified Baseline for fine-grained video retrieval and captioning, achieving competitive performance through two-stage Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). CaRe excels in both generating detailed video descriptions and extracting robust video features.
🚀 State-of-the-art performance on both detailed video captioning and fine-grained video retrieval. CaRe outperforms CLIP-based retrieval models and popular MLLMs in captioning tasks.

Our code is quite simple and easy. Just follow the instructions below and the code will work like magic.
Install the requirements.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Our framework supports auto-loadable inference of all the MLLMs metioned in our paper, including CaRe, LLaVA NeXT Video, MiniCPM-V 2.6, InternVL2, Qwen2-VL and Tarsier. You only need to change the checkpoint path and our model loader will load them automatically.
For Video Captioning Task
from utils.video import read_frames_decord
from models.modeling_captioners import AutoCaptioner
captioner = AutoCaptioner.from_pretrained('path/to/checkpoints/CaRe-7B')
frames = read_frames_decord(video_path='assets/demo.mp4', num_frames=32)
description = captioner.describe(frames.unsqueeze(0))
print(description[0])For Video Retrieval Task
from utils.video import read_frames_decord
from models.modeling_encoders import AutoEncoder
from torch.nn.functional import cosine_similarity
encoder = AutoEncoder.from_pretrained('path/to/checkpoints/CaRe-7B')
frames = read_frames_decord(video_path='assets/demo.mp4', num_frames=32)
text = "This video features a man slicing tomatoes in the kitchen."
vision_emb = encoder.encode_vision(frames.unsqueeze(0))
text_emb = encoder.encode_text(text)
print(f'Vision embedding shape: {vision_emb.shape}')
print(f'Text embedding shape: {text_emb.shape}')
print(f'Cosine similarity: {cosine_similarity(vision_emb, text_emb)}')-
Download data from our huggingface repository.
-
Add our benchmark to
data.config. -
Check the arguments in
scripts/captioning.shorscripts/retrieval.shand run it.
Stage-I
We are preparing for the release of Stage-I training code.
Stage-II
- Download data
mkdir data && wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/princeton-nlp/datasets-for-simcse/resolve/main/nli_for_simcse.csv -O data/nli_for_simcse.csv
- Check the arguments in
scripts/train.shwe prepare for you and run it.
Our framework is designed for our paper, but it is also scalable since we have added many code specification. If you wish to have your retrieval model or caption model evaluated within our framework, please refer to the following guidelines.
- Inherit your model from the
BaseModelinmodels/modeling_basemodels.py, and implement the__init__function. Your model will automatically gain the from_pretrained method. - (Optional) To support all the auto methods, set
ARCHITECTUREin your class property. Make sure there isconfig.jsonin your model path with the structure below (something like transformers models).ARCHITECTUREshould be the same asarchitectures[0]. Then, all the auto methods will load your model according to this architecture.
{
"architectures": [
"CLIPModel"
],
...
}- Inherit your retrieval model from your custom base model and
EncodeMixinin `models/modeling_encoders.py - Implement
encode_visionandencode_textmethod.
- Inherit your caption model from your custom base model and
CaptionMixinin `models/modeling_captioners.py - Implement
describemethod.

