Rossmann is one of the largest drug store chains in Europe with around 56,200 employees and more than 4000 stores across Europe.
Rossmann store managers often have the difficult task of predicting their daily sales up to six weeks in advance. Store sales can be influenced by many factors, including:
- promotions, competition, school and state holidays, seasonality and location,...
Additionally, there are thousands of individual managers predicting sales based on their unique circumstances. As a result, in 2015, Rossmann saw that the accuracy of these prediction results could be quite varied and created a kaggle competition to challenge data scientists to create an efficient model that would help them with this all-important prediction.
The assumptions about the business problem is as follows:
-
"Sales are the lifeblood of a business. It's what helps you pay employees, cover operating expenses, buy more inventory, market new products and attract more investors. Sales forecasting is a crucial part of the financial planning of a business. It's a self-assessment tool that uses past and current sales statistics to intelligently predict future performance."
-
"With an accurate sales forecast in hand, you can plan for the future. If your sales forecast says that during December you make 30 percent of your yearly sales, then you need to ramp up manufacturing in September to prepare for the rush. It might also be smart to invest in more seasonal salespeople and start a targeted marketing campaign right after Thanksgiving. One simple sales forecast can inform every other aspect of your business."
-
"Sales forecasting is one of the most important business processes to running the business. It determines how the company invests and grows and can have a massive impact on company valuation."
References:
- https://money.howstuffworks.com/sales-forecasting1.htm
- https://www.clari.com/blog/the-importance-of-sales-forecasting/
- Business question:
- Forecast store sales in the next 6 weeks
- Understanding the business (it was invented to further contextualize our problem):
- Find out where the root problem comes from → the CFO needs to renovate the stores and he needs to know which ones he should invest the most
- For this, the forecast of 6 weeks of sales seems reasonable as a solution
- Find out where the root problem comes from → the CFO needs to renovate the stores and he needs to know which ones he should invest the most
- Data collection
- Available in kaggle
- Data cleaning
- Description of data
- Knowing the size of the problem we are facing
- Feature engineering
- Create new variables from the originals, aiming at a better visualization of them
- Filtering of variables
- Filter variables based on business bias (data that cannot be used by the company in general, data that will not be available at the time of prediction,...)
- This influences how we will model the algorithm
- Description of data
- Exploratory data analysis( EDA )
- Understand the business from the point of view of data
- Create the feeling, through plots and hypotheses, of which variables would be important for learning the model
- We generate insights, even causing a possible breach of beliefs in other employees
- Data modeling
- We separated the data, but now we need to prepare the data for machine learning models
- Encoding of categorical and numerical variables
- Feature selection using some ML algorithm, in this project it was Boruta
- We see the correlation of the analyzed variable with the answer
- We separated the data, but now we need to prepare the data for machine learning models
- Machine Learning Algorithms
- We initially implemented 1 baseline algorithm, 2 linear and 2 non-linear
- After that we apply crossvalidation to validate the performance of the models we choose
- Algorithm Evaluation
- We analyze the error from the point of view of model performance
- Looking at MPE, RMSE, MAE, MAPE
- We analyze the error from the point of view of model performance
-
Stores with closer competitors should sell less.(common sense)
- FALSE, Stores with CLOSER COMPETITORS sell MORE.
- Is it important for the model? It might be important for the model, but in a weaker way
- FALSE, Stores with CLOSER COMPETITORS sell MORE.
-
Stores with larger assortments should sell more.
- FALSE, because stores with promotions active for a long time sell less after a certain period of promotion.
- Is it important for the model? No, low pearson
- FALSE, because stores with promotions active for a long time sell less after a certain period of promotion.
-
Stores should sell more over the years.
- FALSE, Stores sell less over the years.
- Is it important for the model? Yes, very high correlation
- FALSE, Stores sell less over the years.
Tests were made using different algorithms.
The chosen algorithm was the XGBoost Regressor. In addition, I made a performance calibration on it.
These are the metrics obtained from the test set.
| MAE | MAPE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|
| 664.974996 | 0.097529 | 957.774225 |
The summary below shows the metrics comparison after running a cross validation score with stratified K-Fold with 10 splits in the full data set.
| Model Name | MAE | MAPE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest Regressor | 837.68 +/- 219.1 | 0.12 +/- 0.02 | 1256.08 +/- 320.36 |
| Linear Regression Regularized Model - Lasso | 2117.26 +/- 341.08 | 0.29 +/- 0.01 | 3061.0 +/- 503.47 |
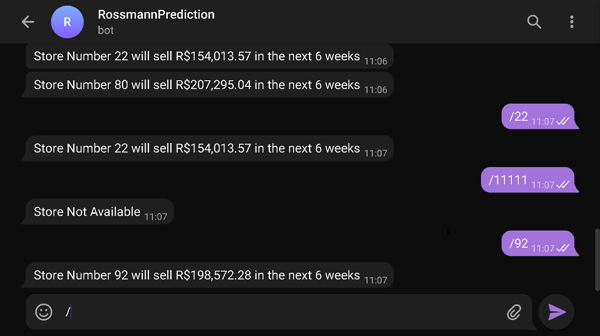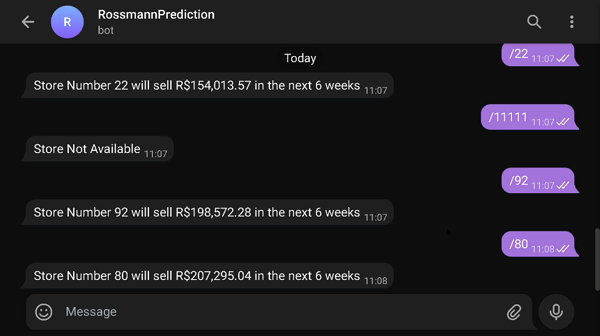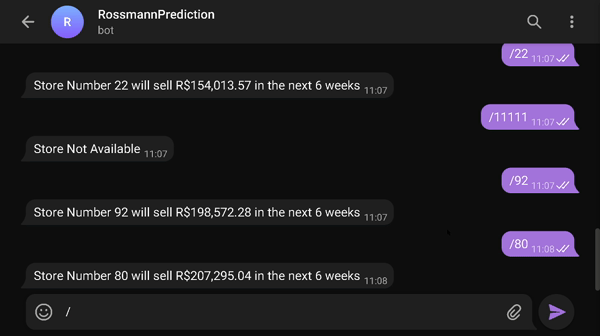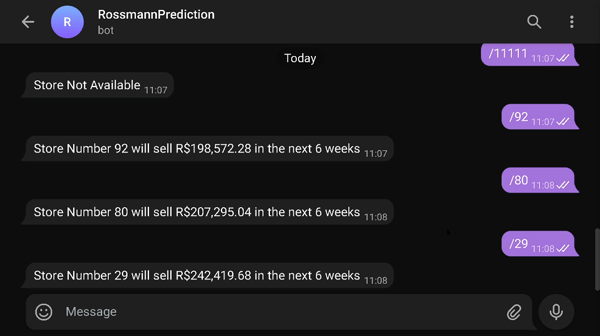
You can see the results of the forecasts on your own phone (or computer) by accessing the bot on the telegram that will make the forecast in real time
- Link to access the results=> t.me/rossmann_pred_edu_bot
- type /number_of_store (1 through 1115) to receive the sales prediction for that store
1. Use more models to lower error metrics .