A malloc implementation
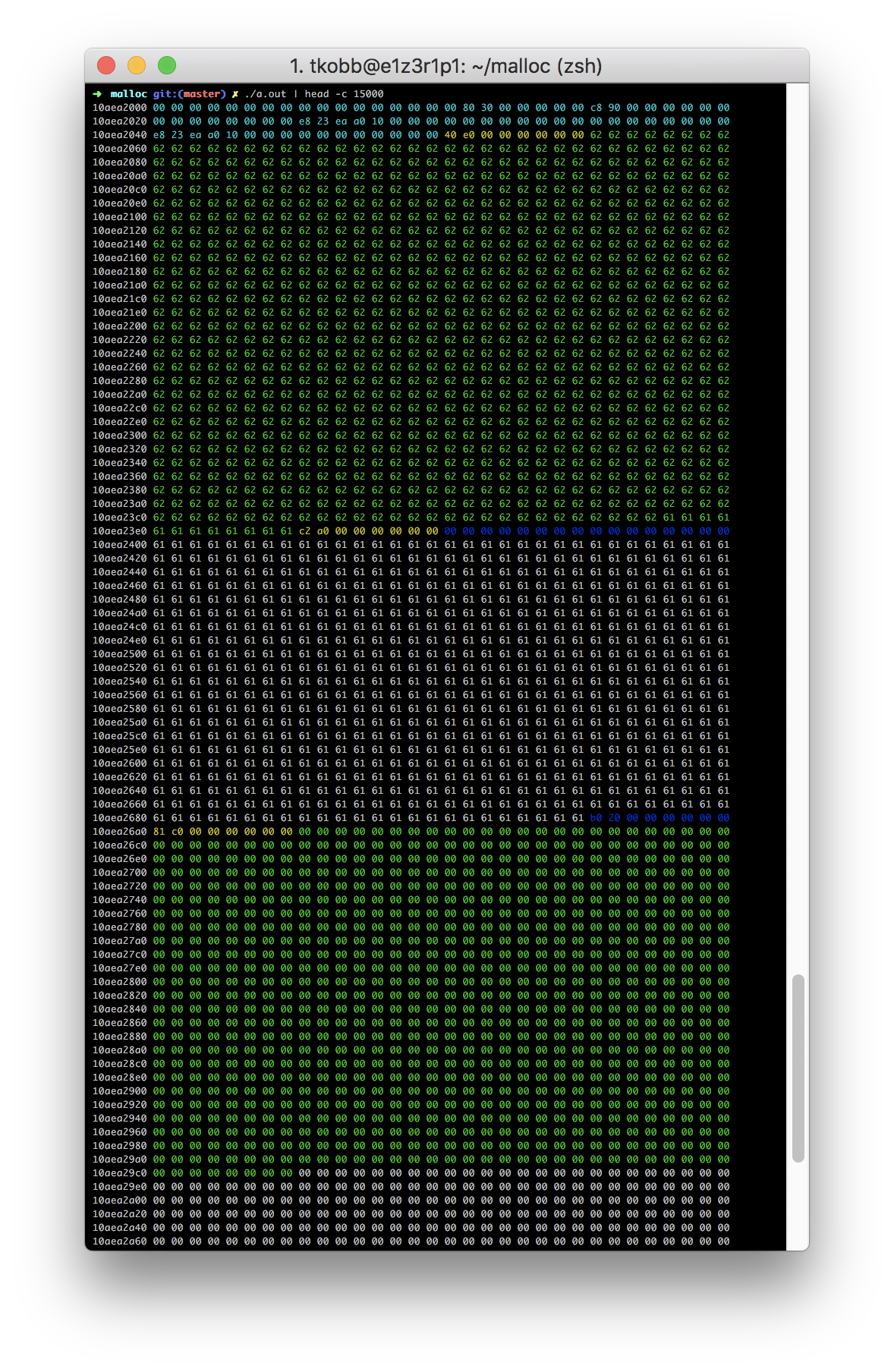
This screenshots displays the memory managed by the library. Yellow represents block headers, green client data and blue free block headers and trailers.
void *malloc(size_t size);
void free(void *ptr);
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t size);
void show_alloc_mem(void); /* print a summary of allocated blocks */
void hexdump_mem(void); /* semantic hexdump of the allocated memory */To create the library:
makeTo run a program, dynamically link it by running
scripts/inject.sh COMMANDOr link with libft_malloc.so.
-
Memory is managed via
mmap(2)andmmunmap(2). -
mmaped areas are managed via the
areastruct andarea__*functions. Areas are a doubly linked list containing individualblocks, which are taken from an availablearea. -
blockshave a 1 word header encoding size, free status, and free status of the previous block. An additional 3 word minimum size is required to store free list nodes. -
free_blocksare doubly-linked list nodes. They have the same header as the underlyingblock, 2 pointers to adjacent free_blocks, an an additional footer encoding the block's size. This footer, in addition toblock.prev_freeallows for linear time coalescing of neighboring blocks. -
Free blocks are stored in an adress-ordered linked list, such that
free_block->prev < free_block < free_block->nextis true for all free blocks for a free list. This ensures that the memory close to the begining of the mmaped areas gets reused sooner, reducing memory fragmentation and improving locality. -
When freeing the last
blockof anarea, the block is destroyed andarea.cur_sizeis reduced, effectively destroying the block. This significantly reduces external fragmentation. -
3 free lists are used. Each list contains blocks of a specific size range (0-255, 256-1023, 1024+).
-
Free blocks are selected on a first fit basis.
-
Memory is defragmented at allocation size. When searching the free list for a block of the requested size, neighboring free blocks are included in the current blocks's size, and merged if the combined size is sufficient.
- Block checksums for fast freeing