- Nomad is a popular workload scheduler for not only containers, but for VMs and static binaries as well.
- Nomad supports a wide range of task drivers such as Docker, Java and binaries running natively on the host operating system.
- Nomad also has a pluggable architecture allowing the addition of new technologies to extend the functionality of Nomad even further.
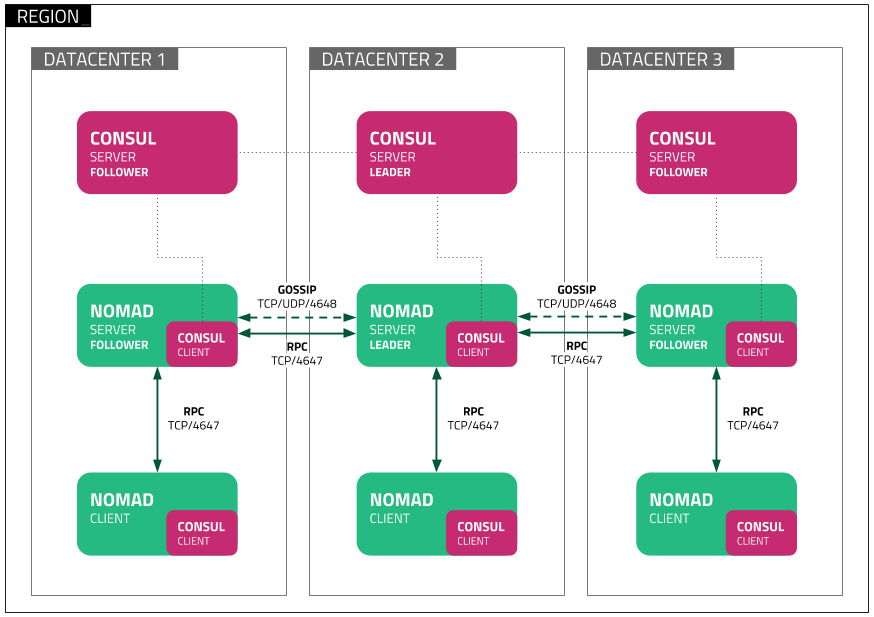
agent: process running in server or client mode. Agents are the basic building blocks of a Nomad cluster. dev-agent is for development and experimental use only.server: a Nomad agent running in server mode:
- Manage all jobs and clients, run evaluations, create task allocations.
- Servers replicate data between each other and perform leader election to ensure HA.
leader: Nomad server that performs the builk of the cluster management.
- Apply plans, deriving Vault tokens for the workloads, and maintaing the cluster state.
follower: Non-leader Nomad servers.client: Nomad agent running in client mode.
- Register with the servers, watch for any work to be assigned, and execute tasks.
- Client <--mutlplexed connection--> server
- Forward RPC calls.
job: define one or more task groups which contain >=1 tasks.
# This declares a job named "docs". There can
# be exactly one job declaration per job filejob "docs" {
job "docs"{
}
job specification (jobspec): define the schema for Nomad jobs.task group: set of tasks that must be run together. A task group is the unit of scheduling, meaning the entire group must run on the same client node and cannot be split. A running instance of a task group is an allocation.
job "docs" {
group "web" {
# All tasks in this group will run on
# the same node
...
}
group "logging" {
# These tasks must also run together
# but may be a different node from web
...
}
}
task driver: represents the basic means of executing your tasks (Docker, QEMU, Java...).task: Tasks are executed by task driver, which allow Nomad to be flexible in the types of tasks it supports. Tasks specify their required task driver, configuration for the driver, constrains and resources required.
job "docs" {
group "example" {
task "server" {
driver = "docker"
}
}
}
allocation: a mapping between a task group in a job and a client node.evaluation: Allocations are created by the Nomad servers as part of scheduling decisions made during an evalution.resources: the requirements a task needs to execute such as memory, network, CPU and more.
job "docs" {
group "example" {
task "server" {
resources {
cpu = 100
memory = 256
network {
mbits = 100
port "http" {}
port "ssh" {
static = 22
}
}
device "nvidia/gpu" {
count = 2
}
}
}
}
}
- http-echo is a tiny go web server that echos what you start it with.
- Check then run first simple job -> access <http://:8080> endpoint.
Hello and welcome to 127.0.0.1 running on port 8080
- Check and edit your current job with scaled up dynamic job version. Nomad will start up 5 instances of the application, and assign a random port to each -> access <http://:> endpoint.
- We're able to access these endpoints, but in the real life scenario, no one does the same -> service discovery -> use Consul - service discovery tool made by Hashicorp. Consul installation isn't coverred in this guide, just do it yourself, it's quite easy as same as Nomad. Check and edit your current job with consul job version.
- While it is relatively easy to query Consul via DNS or API to retrieve these port numbers, web browsers themselves are not able to easily perform this action and route between the various running instances of our application. To solve this limitation, use load balancer -> Fabio. Run fabio job, then fabio consul job version].