diff --git a/dsa/Algorithms/dijkstra.md b/dsa/Algorithms/dijkstra.md
index b7a7b981a..2533663d5 100644
--- a/dsa/Algorithms/dijkstra.md
+++ b/dsa/Algorithms/dijkstra.md
@@ -53,9 +53,9 @@ function Dijkstra(Graph, source):
## Implementing Dijkstra's Algorithm
-### Python Implementation
-
-```python
+
+
+ ``` Python showLineNumbers
import heapq
def dijkstra(graph, start):
@@ -96,11 +96,13 @@ graph = {
}
print(shortest_path(graph, 'A', 'D'))
+
```
+
-### Java Implementation
+
-```java
+``` jsx showLineNumbers
import java.util.*;
public class Dijkstra {
@@ -170,11 +172,12 @@ public class Dijkstra {
}
}
}
-```
-### C++ Implementation
+```
+
-```cpp
+
+```cpp showLineNumbers
#include
#include
#include
@@ -248,11 +251,12 @@ int main() {
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
-```
-### JavaScript Implementation
+```
+
-```javascript
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
function dijkstra(graph, start) {
let distances = {};
let previousNodes = {};
@@ -328,7 +332,10 @@ let graph = {
};
console.log(shortestPath(graph, 'A', 'D'));
+
```
+
+
## Applications of Dijkstra's Algorithm
diff --git a/dsa/Algorithms/hashing.md b/dsa/Algorithms/hashing.md
index 9d64ef340..0e9e95e4c 100644
--- a/dsa/Algorithms/hashing.md
+++ b/dsa/Algorithms/hashing.md
@@ -65,9 +65,9 @@ Hashing is the process of converting input data (keys) into a fixed-size integer
## Implementing Hash Tables
-### Python Implementation
-
-```python
+
+
+```Python showLineNumbers
class HashTable:
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
@@ -105,11 +105,12 @@ ht.insert("banana", 2)
print(ht.lookup("apple")) # Output: 1
ht.delete("apple")
print(ht.lookup("apple")) # Output: None
-```
-### Java Implementation
+```
+
-```java
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
import java.util.LinkedList;
class HashTable {
@@ -173,11 +174,11 @@ class HashTable {
System.out.println(ht.lookup("apple")); // Output: null
}
}
-```
-
-### C++ Implementation
-```cpp
+```
+
+
+```cpp showLineNumbers
#include
#include
#include
@@ -233,11 +234,12 @@ int main() {
cout << ht.lookup("apple") << endl; // Output: -1
return 0;
}
-```
-### JavaScript Implementation
+```
+
-```javascript
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
class HashTable {
constructor(size) {
this.size = size;
@@ -287,7 +289,10 @@ ht.delete("apple");
console.log(ht.lookup("apple"));
// Output: null
+
```
+
+
## Time Complexity Analysis
diff --git a/dsa/Algorithms/prims.md b/dsa/Algorithms/prims.md
index 348976d33..abb099bdb 100644
--- a/dsa/Algorithms/prims.md
+++ b/dsa/Algorithms/prims.md
@@ -45,11 +45,10 @@ function prim(graph, start):
return MST
```
-## Implementation in Various Languages
+
+
-### Python
-
-```python
+```python showLineNubmers
import heapq
def prim(graph, start):
@@ -79,11 +78,13 @@ graph = {
mst = prim(graph, 'A')
print(mst) # Output: [('A', 'B', 1), ('B', 'D', 2), ('B', 'C', 3)]
+
```
+
-### Java
+
-```java
+```jsx showLineNumbers
import java.util.*;
public class Prim {
@@ -131,11 +132,12 @@ public class Prim {
}
}
}
-```
-### C++
+```
+
-```cpp
+
+```cpp showLineNumbers
#include
#include
#include
@@ -191,11 +193,12 @@ int main() {
cout << "[" << edge[0] << ", " << edge[1] << ", " << edge[2] << "]" << endl; // Output: [0, 1, 1], [1, 3, 2], [1, 2, 3]
}
}
-```
-### JavaScript
+```
+
-```javascript
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
@@ -297,7 +300,10 @@ const graph = {
const mst = prim(graph, 'A');
console.log(mst); // Output: [['A', 'B', 1], ['B', 'D', 2], ['B', 'C', 3]]
+
```
+
+
## Example
diff --git a/dsa/Algorithms/searching.md b/dsa/Algorithms/searching.md
index 529b19afc..f539fd2b6 100644
--- a/dsa/Algorithms/searching.md
+++ b/dsa/Algorithms/searching.md
@@ -16,9 +16,9 @@ Linear search, also known as sequential search, is a simple search algorithm tha

-### Python Implementation
-
-```python
+
+
+```python showLineNumbers
def linear_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == target:
@@ -28,11 +28,11 @@ def linear_search(arr, target):
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target = 30
print(linear_search(arr, target)) # Output: 2
-```
-
-### Java Implementation
-```java
+```
+
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
public class LinearSearch {
public static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int target) {
@@ -50,11 +50,12 @@ public class LinearSearch {
System.out.println(linearSearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
}
}
-```
-### C++ Implementation
+```
+
-```cpp
+
+```cpp showLineNumbers
#include
#include
@@ -73,11 +74,11 @@ int main() {
std::cout << linearSearch(arr, target) << std::endl; // Output: 2
return 0;
}
-```
-
-### JavaScript Implementation
-```javascript
+```
+
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
function linearSearch(arr, target) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] === target) {
@@ -90,7 +91,10 @@ function linearSearch(arr, target) {
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
let target = 30;
console.log(linearSearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
+
```
+
+
## 2. Binary Search
@@ -98,9 +102,9 @@ Binary search is a more efficient search algorithm for sorted arrays. It works b
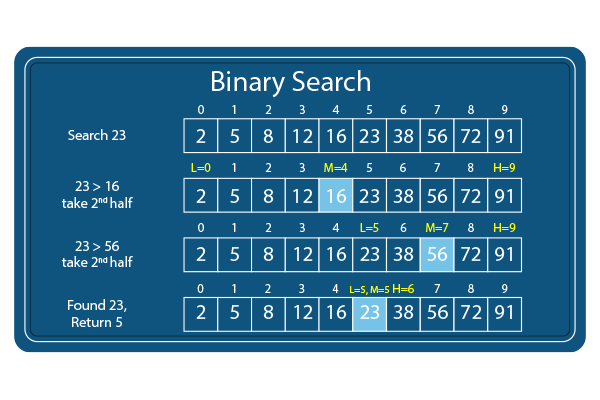
-### Python Implementation
-
-```python
+
+
+```python showLineNumbers
def binary_search(arr, target):
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
@@ -118,11 +122,11 @@ def binary_search(arr, target):
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target = 30
print(binary_search(arr, target)) # Output: 2
-```
-
-### Java Implementation
-```java
+```
+
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
public class BinarySearch {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
@@ -148,11 +152,11 @@ public class BinarySearch {
System.out.println(binarySearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
}
}
-```
-### C++ Implementation
-
-```cpp
+```
+
+
+```cpp showLineNumbers
#include
#include
@@ -179,11 +183,12 @@ int main() {
std::cout << binarySearch(arr, target) << std::endl; // Output: 2
return 0;
}
-```
-### JavaScript Implementation
+```
+
-```javascript
+
+```jsx showLineNumbers
function binarySearch(arr, target) {
let low = 0;
let high = arr.length - 1;
@@ -204,7 +209,10 @@ function binarySearch(arr, target) {
let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
let target = 30;
console.log(binarySearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2
+
```
+
+
## Time Complexity Analysis