-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Description
Commands/shortcuts
Duplicate Object = CTRL + D
Opens reference to documentation = CTRL + '
New Empty GameObject: CTRL + SHIFT + N
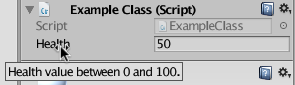
Write "inf" in the inspector textboxes transforms the value to Infinity
Projects Settings
Setup Github for Unity Projects: link
Gitignore for Unity: link
Check Infos: Edit > Project Settings > Input
NavMesh to define the walkable areas in the levels.
Event Systems to detect and handle user input and scripted interaction.
Animator state machine to control and play all of the character animations; including idle, walking and interaction.
Prefab system to save the character so it can be easily added and used in any scene in the game.
Scripting
Event functions / Default Mono Behaviour:
Initialization Events
Awake = The Awake function is called for each object in the scene at the time when the scene loads.
(it is called regardless if the script is enabled or not), all the Awakes will have finished before the first Start is called. This means that code in a Start function can make use of other initializations previously carried out in the Awake phase.
Start = The Start function is called before the first frame or physics update on an object.
Regular Update Events
Update = Update is called before the frame is rendered and also before animations are calculated.
FixedUpdate = FixedUpdate is called just before each physics update. It is important to note that the physics updates and frame updates do not occur with the same frequency.
LateUpdate = Runs at a point after the Update and FixedUpdate functions have been called for all objects in the scene and after all animations have been calculated.
Time and Framerate Management
Time.timeScale = Time Scale property that controls how fast game time proceeds relative to real time. It can produce effects like: Bullet time, slow motion or even stop the game.
void Pause() {
Time.timeScale = 0;
}
void Resume() {
Time.timeScale = 1;
}
Creating and Destroying GameObjects
Instantiate = Create/make a copy of an object (the original object doesn't have to be in the scene).
GameObject enemy;
Instantiate(enemy);
Destroy = will destroy an object after the frame update has finished or optionally after a short time delay.
Destroy(enemy);
Destroy(enemy, .5f);//destroys it after short interval
Destroy(this);//destroy the current script and not the GameObject itself!
Attributes
Attributes are markers that can be placed above a class, property or function in a script to indicate special behaviour.
[System.Serializable] = add to class to make public fields visible in the editor.
[SerializeField] = add to private fields to show them in the editor/inspector.
[HideInInspector] = prevent the property being shown in the inspector, even if it is public.
[Range(float,float)] = displays a slider in the inspector using the defined values.
[Tooltip(string)] = provides information in the inspector about the related field/property.
UI
Unity UI is based on Canvas.
UI Elements have Rect Transform instead of Transform.
It is good practice to add a canvas group to the main Canvas. Canvas group allows UI elements to have an alpha and it allows you to toggle whether they are interactables.
RENDER MODE = The render mode can be set to Screen Space - Overlay so it will fit the screen; Screen Space - Camera which can have UI perspective and World Space, which is for things that are intrinsically within the 3D scene. So for example you might have a speech bubble popping up from a 3D character.
Objects/Components Behaviours
#rigidbody
-->MovePosition
#Vector3
-->normalized
.setActive(bool); // GameObject
.enabled = bool; // component
Unity's coding good practices
Public variables always before private ones.
Use namespaces to separation of concerns.
To add later:
prefabs brief description;
use of forward instead of addForce;
Input.GetAxisRaw() != Input.GetAxis(): There is difference in the return values, check what it is;