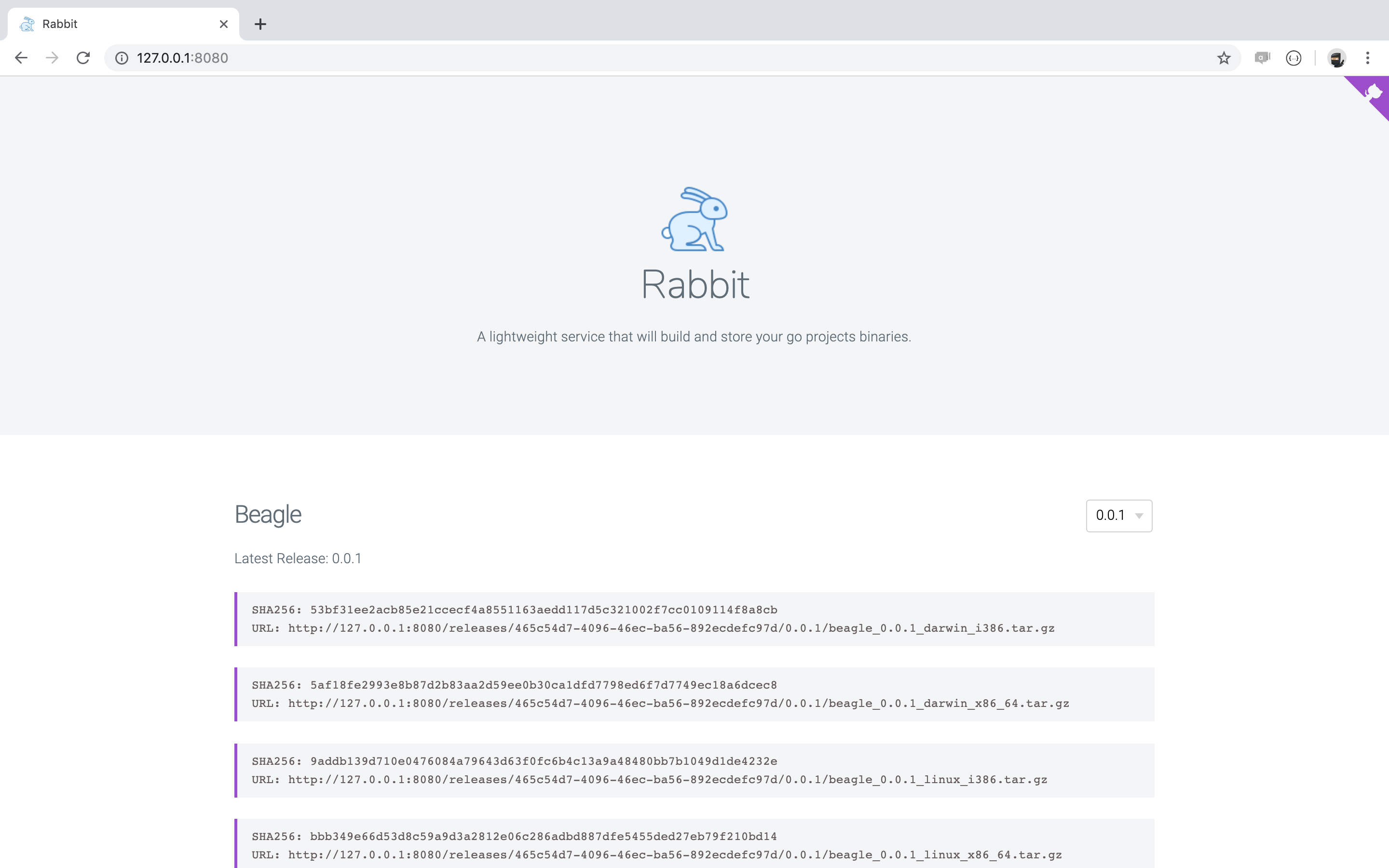
A lightweight service that will build and store your go projects binaries.
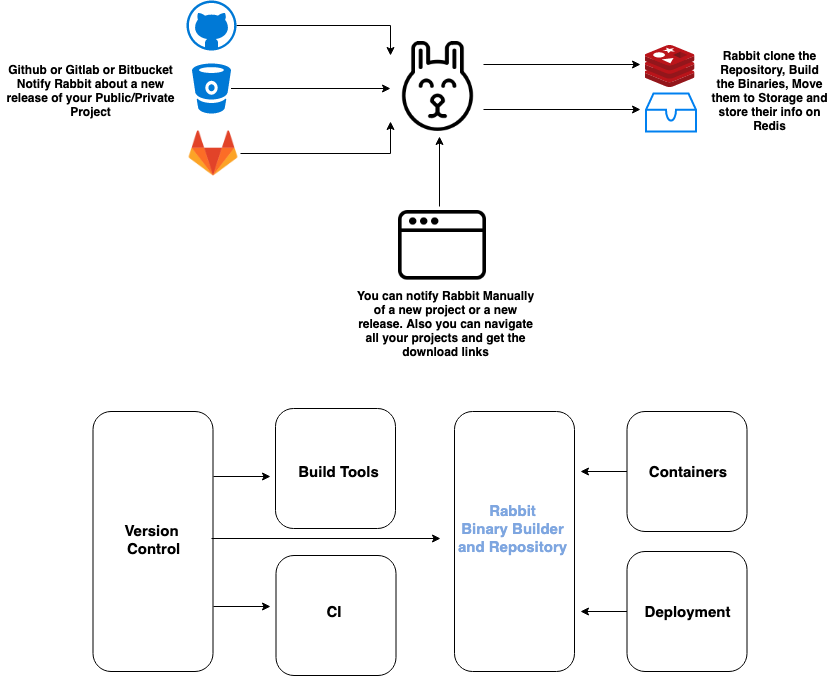
Rabbit is a lightweight service that will build and store your go projects binaries. Once a VCS system (Github, Gitlab, Bitbucket or Bitbucket Server) notifies rabbit of a new release, it clones the project, builds different binaries and publishes them.
Rabbit uses Go Modules to manage dependencies. First Create a prod config file.
$ git clone https://github.com/Clivern/Rabbit.git
$ cp config.dist.yml config.prod.ymlThen add your default configs. You probably wondering how the following configs even work! let's pick one and explain.
The item mode: ${RABBIT_APP_MODE:-dev} means that the mode is dev unless environment variable RABBIT_APP_MODE is defined. so you can always override the value by defining the environment variable export RABBIT_APP_MODE=prod. and same for others
# General App Configs
app:
# Env mode (dev or prod)
mode: ${RABBIT_APP_MODE:-dev}
# HTTP port
port: ${RABBIT_APP_PORT:-8080}
# App URL
domain: ${RABBIT_APP_DOMAIN:-http://127.0.0.1:8080}
# TLS configs
tls:
status: ${RABBIT_APP_TLS_STATUS:-off}
pemPath: ${RABBIT_APP_TLS_PEMPATH:-cert/server.pem}
keyPath: ${RABBIT_APP_TLS_KEYPATH:-cert/server.key}
# Redis Configs
redis:
addr: ${RABBIT_REDIS_ADDR:-localhost:6379}
password: ${RABBIT_REDIS_PASSWORD:- }
db: ${RABBIT_REDIS_DB:-0}
# Message Broker Configs
broker:
# Broker driver (native or redis)
driver: ${RABBIT_BROKER_DRIVER:-native}
# Native driver configs
native:
# Queue max capacity
capacity: ${RABBIT_BROKER_NATIVE_CAPACITY:-50}
# Number of concurrent workers
workers: ${RABBIT_BROKER_NATIVE_WORKERS:-1}
# Redis configs
redis:
channel: ${RABBIT_BROKER_REDIS_CHANNEL:-rabbit}
# Log configs
log:
# Log level, it can be debug, info, warn, error, panic, fatal
level: ${RABBIT_LOG_LEVEL:-warn}
# output can be stdout or abs path to log file /var/logs/rabbit.log
output: ${RABBIT_LOG_OUTPUT:-stdout}
# Format can be json
format: ${RABBIT_LOG_FORMAT:-json}
# Release configs
releases:
# Releases absolute path
path: ${RABBIT_RELEASES_PATH:-/app/var/releases}
name: ${RABBIT_RELEASES_NAME:-"[.Tag]"}
# Build configs
build:
# Build absolute path
path: ${RABBIT_BUILD_PATH:-/app/var/build}
# Number of parallel builds
parallelism: ${RABBIT_BUILD_PARALLELISM:-1}
# Application Database
database:
# Database driver (redis)
driver: ${RABBIT_DATABASE_DRIVER:-redis}
# Redis
redis:
hash_prefix: ${RABBIT_DATABASE_REDIS_HASH_PREFIX:-rabbit_}
# Third Party API Integration
integrations:
# Github Configs
github:
# Webhook URI (Full URL will be app.domain + webhook_uri)
webhook_uri: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITHUB_WEBHOOK_URI:-/webhook/github}
# Webhook Secret (From Repo settings page > Webhooks)
webhook_secret: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITHUB_WEBHOOK_SECRET:- }
# whether to use ssh or https to clone
clone_with: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITHUB_CLONE_WITH:-https}
# HTTPS URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
https_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITHUB_HTTPS_FORMAT:-https://github.com/[.RepoFullName].git}
# SSH URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
ssh_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITHUB_SSH_FORMAT:[email protected]:[.RepoFullName].git}
# Bitbucket Configs
bitbucket:
# Webhook URI (Full URL will be app.domain + webhook_uri)
webhook_uri: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_WEBHOOK_URI:-/webhook/bitbucket}
# whether to use ssh or https to clone
clone_with: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_CLONE_WITH:-https}
# HTTPS URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
https_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_HTTPS_FORMAT:-https://bitbucket.org/[.RepoFullName].git}
# SSH URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
ssh_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_SSH_FORMAT:[email protected]:[.RepoFullName].git}
bitbucket_server:
# Webhook URI (Full URL will be app.domain + webhook_uri)
webhook_uri: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_SERVER_WEBHOOK_URI:-/webhook/bitbucket-server}
# Webhook Secret (From Repo settings page > Webhooks)
webhook_secret: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_SERVER_WEBHOOK_SECRET:- }
# whether to use ssh or https to clone
clone_with: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_SERVER_CLONE_WITH:-https}
# HTTPS URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
https_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_SERVER_HTTPS_FORMAT:-https://git.bitbucket.com/scm/[.RepoFullName].git}
# SSH URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
ssh_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_BITBUCKET_SERVER_SSH_FORMAT:-ssh://[email protected]/[.RepoFullName].git}
gitlab:
# Webhook URI (Full URL will be app.domain + webhook_uri)
webhook_uri: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITLAB_WEBHOOK_URI:-/webhook/gitlab}
# Webhook Secret (From Repo settings page > Webhooks)
webhook_secret: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITLAB_WEBHOOK_SECRET:- }
# whether to use ssh or https to clone
clone_with: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITLAB_CLONE_WITH:-https}
# HTTPS URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
https_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITLAB_HTTPS_FORMAT:-https://gitlab.com/[.RepoFullName].git}
# SSH URL format, Full name will be something like Clivern/Rabbit
ssh_format: ${RABBIT_INTEGRATION_GITLAB_SSH_FORMAT:[email protected]:[.RepoFullName].git}And then run the application.
$ go build rabbit.go
$ ./rabbit
// OR
$ go run rabbit.go
// To Provide a custom config file
$ ./rabbit -config=/custom/path/config.prod.yml
$ go run rabbit.go -config=/custom/path/config.prod.ymlRabbit needs a decent resources to be able to work properly because the build process itself done by goreleaser and it consumes a lot. So keep build.parallelism equal 1 and increase if you have more resources and would like to speed the build process.
Make sure you have git, golang 1.12 and goreleaser installed, and make goreleaser executable from everywhere.
# To download the latest goreleaser binary for linux (https://github.com/goreleaser/goreleaser/releases)
$ curl -sL https://github.com/goreleaser/goreleaser/releases/download/v0.116.0/goreleaser_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz | tar xzAlso make sure you are able to clone all your repositories in a non-interactive way. Just configure ssh-key and add the remote VCS to your known hosts.
Then download the latest Rabbit binary.
$ curl -sL https://github.com/Clivern/Rabbit/releases/download/x.x.x/rabbit_x.x.x_OS.tar.gz | tar xzCreate your config file as explained before on development part and run rabbit with systemd or anything else you prefer.
$ ./rabbit -config=/custom/path/config.prod.yml
Running rabbit with docker-compose is pretty straightforward.
$ git clone https://github.com/Clivern/Rabbit.git
$ cd Rabbit/deployments/docker
$ docker-compose build
$ docker-compose up -dDocker will mount you host server ~/.ssh directory in order to be able to clone repositories that need ssh key. Please make sure it has the right permissions and also remote VCS added to known hosts. otherwise rabbit will stuck on git interactive clone.
For transparency into our release cycle and in striving to maintain backward compatibility, Rabbit is maintained under the Semantic Versioning guidelines and release process is predictable and business-friendly.
See the Releases section of our GitHub project for changelogs for each release version of Rabbit. It contains summaries of the most noteworthy changes made in each release.
If you have any suggestions, bug reports, or annoyances please report them to our issue tracker at https://github.com/clivern/rabbit/issues
If you discover a security vulnerability within Rabbit, please send an email to [email protected]
We are an open source, community-driven project so please feel free to join us. see the contributing guidelines for more details.
© 2019, Clivern. Released under MIT License.
Rabbit is authored and maintained by @Clivern.