参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们受益!
题目描述:
给定一个由 1(陆地)和 0(水)组成的矩阵,你需要计算岛屿的数量。岛屿由水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成,并且四周都是水域。你可以假设矩阵外均被水包围。
输入描述:
第一行包含两个整数 N, M,表示矩阵的行数和列数。
后续 N 行,每行包含 M 个数字,数字为 1 或者 0。
输出描述:
输出一个整数,表示岛屿的数量。如果不存在岛屿,则输出 0。
输入示例:
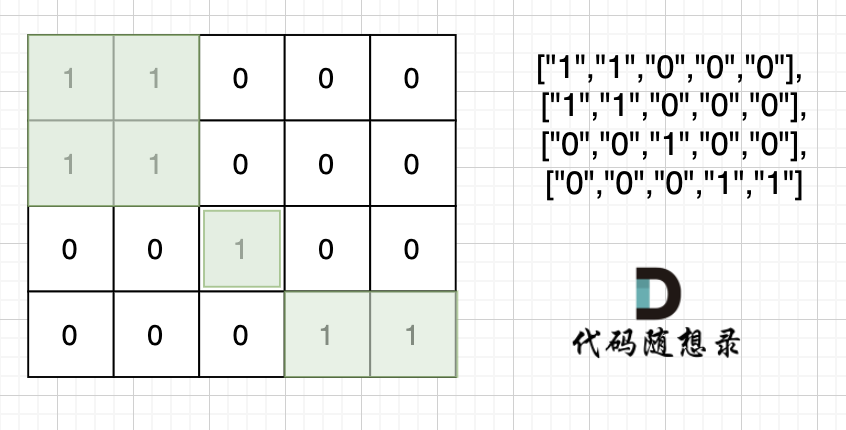
4 5
1 1 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1
输出示例:
3
提示信息
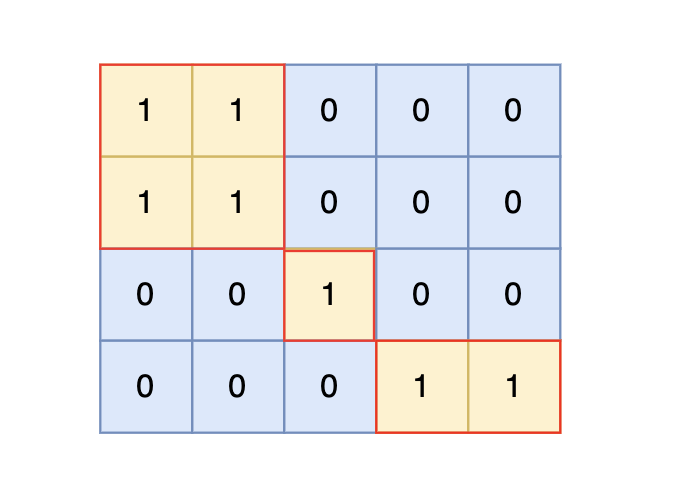
根据测试案例中所展示,岛屿数量共有 3 个,所以输出 3。
数据范围:
- 1 <= N, M <= 50
注意题目中每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
也就是说斜角度链接是不算了, 例如示例二,是三个岛屿,如图:
这道题题目是 DFS,BFS,并查集,基础题目。
本题思路:遇到一个没有遍历过的节点陆地,计数器就加一,然后把该节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上。
再遇到标记过的陆地节点和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量。
那么如果把节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上呢,就可以使用 DFS,BFS或者并查集。
如果不熟悉广搜,建议先看 广搜理论基础。
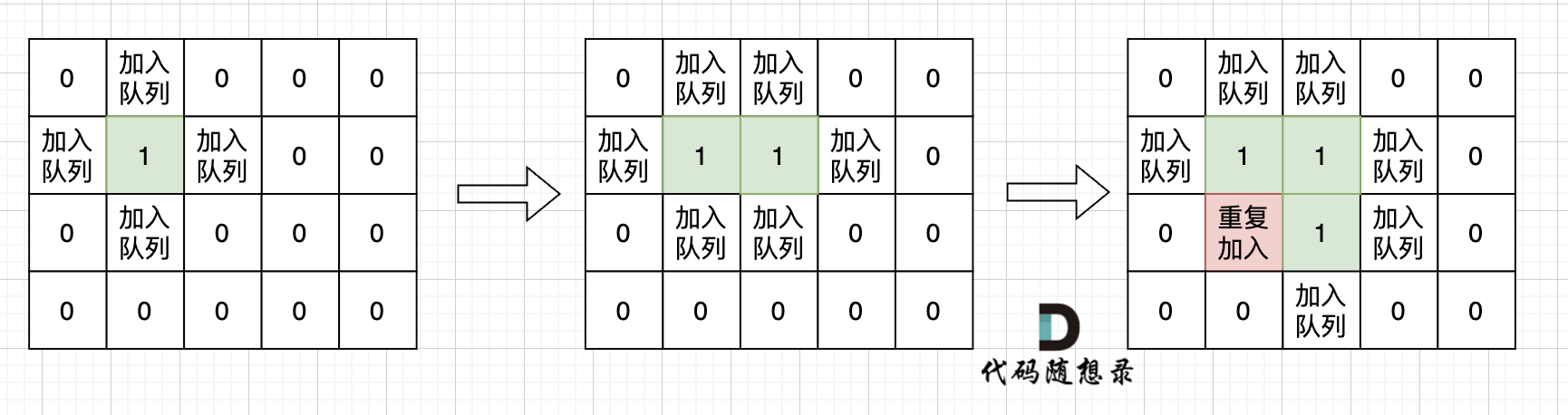
不少同学用广搜做这道题目的时候,超时了。 这里有一个广搜中很重要的细节:
根本原因是只要 加入队列就代表 走过,就需要标记,而不是从队列拿出来的时候再去标记走过。
很多同学可能感觉这有区别吗?
如果从队列拿出节点,再去标记这个节点走过,就会发生下图所示的结果,会导致很多节点重复加入队列。
超时写法 (从队列中取出节点再标记,注意代码注释的地方)
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
visited[curx][cury] = true; // 从队列中取出在标记走过
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
}
}
}
}加入队列 就代表走过,立刻标记,正确写法: (注意代码注释的地方)
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(vector<vector<char>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == '1') {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
}
}
}
}以上两个版本其实,其实只有细微区别,就是 visited[x][y] = true; 放在的地方,这取决于我们对 代码中队列的定义,队列中的节点就表示已经走过的节点。 所以只要加入队列,立即标记该节点走过。
本题完整广搜代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
visited[nextx][nexty] = true; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> grid(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> grid[i][j];
}
}
vector<vector<bool>> visited(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
bfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
}
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int[][] dir = { {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} }; // 四个方向
public static void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.length || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].length) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (!visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = true;
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
visited[i][j] = true;
result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
dfs(grid, visited, i, j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
def dfs(grid, visited, x, y):
dir = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)] # 四个方向
for d in dir:
nextx, nexty = x + d[0], y + d[1]
if 0 <= nextx < len(grid) and 0 <= nexty < len(grid[0]):
if not visited[nextx][nexty] and grid[nextx][nexty] == 1: # 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = True
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty)
def main():
n, m = map(int, input().split())
grid = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
result = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if not visited[i][j] and grid[i][j] == 1:
visited[i][j] = True
result += 1 # 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
dfs(grid, visited, i, j) # 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 True
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
var dir = [4][2]int{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}} // 四个方向
func dfs(grid [][]int, visited [][]bool, x, y int) {
for i := 0; i < 4; i++ {
nextx := x + dir[i][0]
nexty := y + dir[i][1]
if nextx < 0 || nextx >= len(grid) || nexty < 0 || nexty >= len(grid[0]) {
continue // 越界了,直接跳过
}
if !visited[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 1 { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
dfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty)
}
}
}
func main() {
reader := bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
var n, m int
fmt.Scanf("%d %d", &n, &m)
grid := make([][]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
grid[i] = make([]int, m)
line, _ := reader.ReadString('\n')
line = strings.TrimSpace(line)
elements := strings.Split(line, " ")
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
grid[i][j], _ = strconv.Atoi(elements[j])
}
}
visited := make([][]bool, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
visited[i] = make([]bool, m)
}
result := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < m; j++ {
if !visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1 {
visited[i][j] = true
result++ // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
dfs(grid, visited, i, j) // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
}
}
}
fmt.Println(result)
}
const r1 = require('readline').createInterface({ input: process.stdin });
// 创建readline接口
let iter = r1[Symbol.asyncIterator]();
// 创建异步迭代器
const readline = async () => (await iter.next()).value;
let graph
let N, M
let visited
let result = 0
const dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]
// 读取输入,初始化地图
const initGraph = async () => {
let line = await readline();
[N, M] = line.split(' ').map(Number);
graph = new Array(N).fill(0).map(() => new Array(M).fill(0))
visited = new Array(N).fill(false).map(() => new Array(M).fill(false))
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
line = await readline()
line = line.split(' ').map(Number)
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
graph[i][j] = line[j]
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 从(x, y)开始广度优先遍历
* @param {*} graph 地图
* @param {*} visited 访问过的节点
* @param {*} x 开始搜索节点的下标
* @param {*} y 开始搜索节点的下标
* @return {*}
*/
const bfs = (graph, visited, x, y) => {
let queue = []
queue.push([x, y])
visited[x][y] = true //只要加入队列就立刻标记为访问过
while (queue.length) {
let [x, y] = queue.shift()
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let nextx = x + dir[i][0]
let nexty = y + dir[i][1]
if(nextx < 0 || nextx >= N || nexty < 0 || nexty >= M) continue
if(!visited[nextx][nexty] && graph[nextx][nexty] === 1){
queue.push([nextx, nexty])
visited[nextx][nexty] = true
}
}
}
}
(async function () {
// 读取输入,初始化地图
await initGraph()
// 统计岛屿数
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && graph[i][j] === 1) {
// 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
result++
// 广度优先遍历,将相邻陆地标记为已访问
bfs(graph, visited, i, j)
}
}
}
console.log(result);
})()<?php
function dfs($grid, &$visited, $x, $y) {
$dir = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]; // 四个方向
foreach ($dir as $d) {
$nextx = $x + $d[0];
$nexty = $y + $d[1];
if ($nextx < 0 || $nextx >= count($grid) || $nexty < 0 || $nexty >= count($grid[0])) {
continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
}
if (!$visited[$nextx][$nexty] && $grid[$nextx][$nexty] == 1) { // 没有访问过的 同时 是陆地的
$visited[$nextx][$nexty] = true;
dfs($grid, $visited, $nextx, $nexty);
}
}
}
function main() {
fscanf(STDIN, "%d %d", $n, $m);
$grid = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
$grid[$i] = array_map('intval', explode(' ', trim(fgets(STDIN))));
}
$visited = array_fill(0, $n, array_fill(0, $m, false));
$result = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
for ($j = 0; $j < $m; $j++) {
if (!$visited[$i][$j] && $grid[$i][$j] == 1) {
$visited[$i][$j] = true;
$result++; // 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1
dfs($grid, $visited, $i, $j); // 将与其链接的陆地都标记上 true
}
}
}
echo $result . PHP_EOL;
}
main();
?>