A best practice in continuous integration pipelines is to "only build packages once" and then consume that same version of the produced artifacts in later steps of the pipeline (e.g. app deployment, functional/integration tests).
In order to implement this pattern in a pipeline, integration with artifacts repositories are commonly used.
This article provides a sample for the integration of JFrog Artifactory, a popular artifact management software in the market, with a Concourse pipeline.
The example uses the Artifactory resource to deploy and retrieve artifacts to/from an Artifactory server.
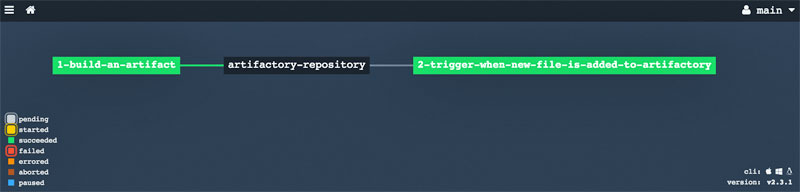
This pipeline implements the pattern of (1) saving a produced versioned build artifact to a repository/folder in Artifactory and (2) retrieving the same file in a subsequent pipeline step, which is triggered once a new file version is detected in the Artifactory repository/folder.
resource_types:
- name: artifactory
type: docker-image
source:
repository: pivotalservices/artifactory-resource
resources:
- name: artifactory-repository
type: artifactory
check_every: 1m
source:
endpoint: http://ARTIFACTORY-HOST-NAME-GOES-HERE:8081/artifactory
repository: "/repository-name/sub-folder"
regex: "myapp-(?<version>.*).txt"
username: YOUR-ARTIFACTORY-USERNAME
password: YOUR-ARTIFACTORY-PASSWORD
jobs:
- name: 1-build-an-artifact
plan:
- task: create-artifact
config:
platform: linux
image_resource:
type: docker-image
source:
repository: ubuntu
outputs:
- name: build
run:
path: sh
args:
- -exc
- |
echo "This is my file content." > ./build/myapp-$(date +"%Y%m%d%H%S").txt
find .
- put: artifactory-repository
params: { file: ./build/myapp-*.txt }
- name: 2-trigger-when-new-file-is-added-to-artifactory
plan:
- get: artifactory-repository
trigger: true
passed:
- 1-build-an-artifact
- task: use-new-file
config:
platform: linux
image_resource:
type: docker-image
source:
repository: ubuntu
inputs:
- name: artifactory-repository
run:
path: cat
args:
- "./artifactory-repository/myapp*.txt"
This pipeline definition file can also be downloaded from this repository.
- An instance of Concourse installed up-and-running.
- The Concourse Fly command line interface installed on your local machine.
- A JFrog Artifactory server up-and-running.
For local tests, you can run Artifactory as a Docker image.
-
Download the provided sample pipeline.yml
-
Edit pipeline.yml and update the parameters for the artifactory-repository definition:
- Replace "ARTIFACTORY-HOST-NAME-GOES-HERE:8081" with the hostname and port number of the Artifactory server. e.g.
http://192.168.99.100:8081/artifactory - Replace "/repository-name/sub-folder" with the location of the files in Artifactory. e.g. /ext-release-local/myapp
- Replace "/repository-name/sub-folder" with the location of the files in Artifactory. e.g.
/ext-release-local/myapp - Update the regex property with the expression that represents the file name of your artifact along with the location of its version information. e.g
my-artifact-(?<version>.*)-release.zip - Replace "YOUR-ARTIFACTORY-USERNAME" and "YOUR-ARTIFACTORY-PASSWORD" with the username and password (respectively) authorized to deploy files to Artifactory.
-
Configure the sample pipeline in Concourse with the fly command:
fly -t set-pipeline -p artifactory-pipeline -c pipeline.yml -
Access to the Concourse web interface, click on the list of pipelines, unpause the artifactory-pipeline and then click on its link to visualize its pipeline diagram
-
To execute the pipeline, click on the
1-build-an-artifactjob and then click on the+sign to execute the pipeline.
After job 1-build-an-artifact is executed, you should see a new version of the created file in the Artifactory server. Subsequently, you should see job 2-trigger-when-new-file-is-added-to-artifactory automatically triggered to retrieve that latest file version from Artifactory.